diff --git a/docs/2a/ece240.md b/docs/2a/ece240.md
index 58cb38f..4b754a7 100644
--- a/docs/2a/ece240.md
+++ b/docs/2a/ece240.md
@@ -155,3 +155,55 @@ The input resistance of common amplifiers is infinity.
 (Source: Wikimedia Commons)
As $V_{gs}$ is not necessarily zero, dependent sources must be left in when solving for output resistance, and so a small test source at the point of interest is required.
+
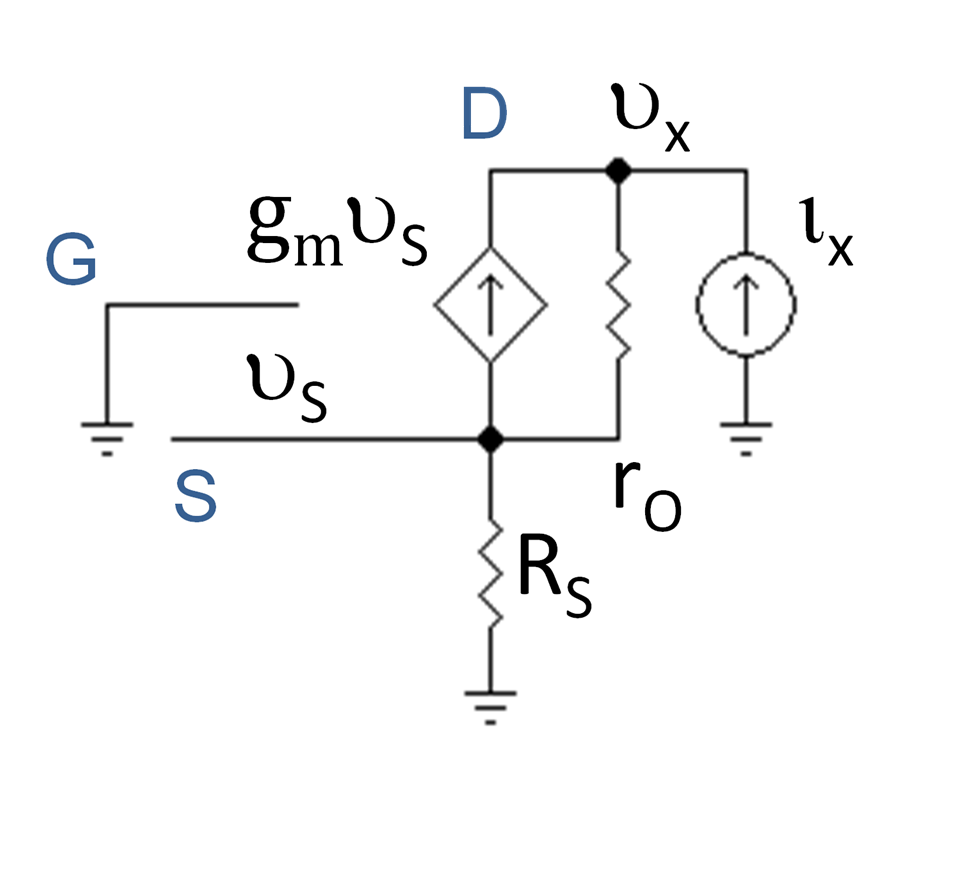
+### Common-gate amplifiers
+
+These can be represented by either the T-model or pi-model. The gate of the transistor is grounded.
+
+$$
+A_{VO}=g_mR_d \\
+G_V=\frac{V_o}{V_{sig}}=g_mR_d\left(\frac{1}{1+g_mR_{sig}}\right)
+$$
+
+
(Source: Wikimedia Commons)
As $V_{gs}$ is not necessarily zero, dependent sources must be left in when solving for output resistance, and so a small test source at the point of interest is required.
+
+### Common-gate amplifiers
+
+These can be represented by either the T-model or pi-model. The gate of the transistor is grounded.
+
+$$
+A_{VO}=g_mR_d \\
+G_V=\frac{V_o}{V_{sig}}=g_mR_d\left(\frac{1}{1+g_mR_{sig}}\right)
+$$
+
+ +
+
+
+ +
+### Differential pairs
+
+These are used at the input of opamps.
+
+In **differential mode,** assuming $Q_1=Q_2$:
+
+$V_{in}^+=-V_{in}^-=\frac{V_d}{2}$, so the current going down from both gates is equal $i_{gs1}=-i_{gs2}$. This means that node before $R_E$ is effectively ground, so the circuit can be split into two common source circuits.
+
+$$G_D=\frac{V_o^--V_o^+}{V_d}=\frac{R_{C1}g_m}{1}=-\frac{-R_{C1}}{r_m}$$
+
+
+
+### Differential pairs
+
+These are used at the input of opamps.
+
+In **differential mode,** assuming $Q_1=Q_2$:
+
+$V_{in}^+=-V_{in}^-=\frac{V_d}{2}$, so the current going down from both gates is equal $i_{gs1}=-i_{gs2}$. This means that node before $R_E$ is effectively ground, so the circuit can be split into two common source circuits.
+
+$$G_D=\frac{V_o^--V_o^+}{V_d}=\frac{R_{C1}g_m}{1}=-\frac{-R_{C1}}{r_m}$$
+
+ +
+In **common mode**:
+
+$V_{in}^+=V_{in}^-$
+
+$$G_{CM}=-\frac{R_D}{r_m+R_S+2R_C}$$
+
+The **common-mode rejection ratio** is:
+
+$$\frac{G_D}{G_{CM}}=1+\frac{2R_C}{r_m+R_s}$$
+
+## MOSFET biasing
+
+To bias a MOSFET:
+
+- the transistor must be on: $V_{GS}>V_t$
+- the transistor must be saturated $V_{DS} > (V_{GS}-V_t)$
+
+$$V_{GS}=V_G-R_EI_D$$
+
+This is a negative feedback loop that forces a constant $I_D$.
+
+
+
+In **common mode**:
+
+$V_{in}^+=V_{in}^-$
+
+$$G_{CM}=-\frac{R_D}{r_m+R_S+2R_C}$$
+
+The **common-mode rejection ratio** is:
+
+$$\frac{G_D}{G_{CM}}=1+\frac{2R_C}{r_m+R_s}$$
+
+## MOSFET biasing
+
+To bias a MOSFET:
+
+- the transistor must be on: $V_{GS}>V_t$
+- the transistor must be saturated $V_{DS} > (V_{GS}-V_t)$
+
+$$V_{GS}=V_G-R_EI_D$$
+
+This is a negative feedback loop that forces a constant $I_D$.
+
+ +
+With two DC supplies ($-V_{EE}, V_{DD}$), having an $R_G$ results in:
+
+$$I_D=\frac{-V_{EE}}{R_S}-\frac{V_{GS}}{R_S}$$
+
+With two DC supplies ($-V_{EE}, V_{DD}$), having an $R_G$ results in:
+
+$$I_D=\frac{-V_{EE}}{R_S}-\frac{V_{GS}}{R_S}$$
 +
+With two DC supplies ($-V_{EE}, V_{DD}$), having an $R_G$ results in:
+
+$$I_D=\frac{-V_{EE}}{R_S}-\frac{V_{GS}}{R_S}$$
+
+With two DC supplies ($-V_{EE}, V_{DD}$), having an $R_G$ results in:
+
+$$I_D=\frac{-V_{EE}}{R_S}-\frac{V_{GS}}{R_S}$$