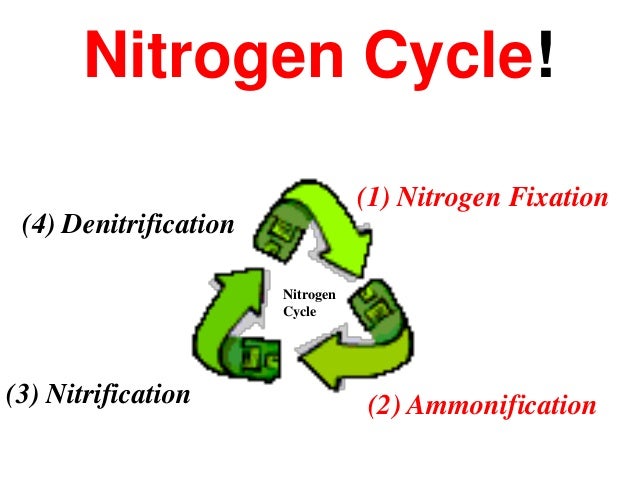
 ### Nitrogen Fixation
@@ -378,9 +380,32 @@ efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic
* Heavy precipitation on leeward side of mountains
* `Species` Elk, cougar, large coniferous trees, ferns.
+## Biodiversity
+- The importance
+
+
## Introducing Ecosystems
- Most ecosystems are **SUSTAINABLE**.
+
### Nitrogen Fixation
@@ -378,9 +380,32 @@ efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic
* Heavy precipitation on leeward side of mountains
* `Species` Elk, cougar, large coniferous trees, ferns.
+## Biodiversity
+- The importance
+
+
## Introducing Ecosystems
- Most ecosystems are **SUSTAINABLE**.
+| Ecosystem | Key abiotic factors | Human action and result | +
|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial Ecosystems | +Light availability Water availability Nutrient availability Temperature |
+Clear-cutting and fire remove shade and expose the remaining organisms to much more light Damming rivers and draining swamps and marshes change water availability. Irrigation increases water availability Farming practices may increase or decrease nutrient levels in the soil. Global warming is decreasing suitable habitat for many cool-adapted species. |
+
| Aquatic Ecosystems | +Light availability Nutrient availability Acidity Temperature Salinity |
+Activities that increase erosion or stir up the bottom cloud the water and reduce light penetration. Nutrient runoff from agriculture and urban enviornments increases the nutrient content of surface water and groundwater, causing algal blooms Acidic air pollution results in acid precipitation. Carbon dioxide emissions produced by the burning of fossil fuels are increasing the acidity of the oceans. Industries and power plants release heated waste water into lakes and rivers, killing fish and other organisms. Salting highways and long-term irrigation practices can cause salt to accumlate. |
+