diff --git a/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 1: Chemistry.md b/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 1: Chemistry.md
index f5cdb43..aa92f27 100644
--- a/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 1: Chemistry.md
+++ b/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 1: Chemistry.md
@@ -61,6 +61,7 @@
- They are dull, bad conductors - insulators
- Tend to gain electrons
- The have a strong hold on electrons
+- Usually non-ductile nor malleable
## Bonds
- An ionic bond is a bond between a negative ion and a positive ion (so a anion and a cation)
@@ -70,7 +71,7 @@
- An cation is formed when an particle loses electrons
- We can use modesl(e.g Lewis dot diagrams) to show bonding
- Atoms will lose or gain electrons to achieve noble gas $`e^-`$ configuration $`\rightarrow`$ The most common stable ion. (eg, if $`Na`$ loses electrons, it becomes like $`Ne`$, if $`Cl`$ gains an electron, it becomes like $`Ar`$)
-- To show that atoms are different than ions, we put square brackets around it $`[Na]`$, then we put superscript on the top right to show its charge, $`[Na]^+`$ (if the charge is only a $`\pm 1`$, we just put a $`+`$ instead of $`+1`$)
+- To show that atoms are different than ions, we put square brackets around it $`[Na]`$, then we put superscript on the top right to show its charge, $`[Na]^+`$ (if the charge is only a $`\pm 1`$, we just put a $`+`$ instead of $`1+`$)
## Non Metal Ionic Names
|Name|Name|
@@ -110,7 +111,7 @@
- `halogens`
- `noble gases`
-- Going down diagonally from aluminium, we get a pattern of 3+, 2+, 1+ of charge. Aluminium has a charge of 3+, Zinc has a charge of 2+, and silver has a charge of 1+, and they
+- Going down diagonally from aluminium, we get a pattern of $`3+`$, $`2+`$, $`1+`$ of charge. Aluminium has a charge of $`3+`$, Zinc has a charge of $`2+`$, and silver has a charge of $`1+`$, and they
are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
- If there is more than one polyatomic ion in a formula unit, then surround the ion with brackets
- Oxyanion are negative ions with oxygen in them
@@ -141,14 +142,14 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|**Hypo**chlor**ite**|(has two less oxygens than the parent)|$`ClO^-`$|
- Note that the charge remains the same
-- Polyatomic ions in the same group on the periodic table from similar polyatomic ions
+- Polyatomic ions in the same group on the periodic table form similar polyatomic ions
|**Chlorate**|$`ClO_3^-`$|
|:-----------|:----------|
|Bromate|$`BrO_3^-`$|
## Acidic Oxyanions
-- Each hydrogen added to a polyatomic ion increases the charge by one, and c hanges the name:
+- Each hydrogen added to a polyatomic ion increases the charge by one, and changes the name:
|Name|Chemical Formula|
|:---|:---------------|
@@ -168,9 +169,33 @@ we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
- Atoms fill their valence shells to form molecules
- Double bond between oxygen atoms in an oxygen molecule
-|Compound|State at Room Temperature|Solubility In Water|Conductivity Of Solution|Ionic Or Molecular|
-|:-------|:------------------------|:------------------|:-----------------------|:-----------------|
-|ammonium chloride|solid|soluable, overtime the substance starts to get smaller and disappears|colourless|ionic|
-|copper|
-|
+## Properties Of Ionic And Molecular Compounds
+|Compound|State at Room Temperature|Solubility In Water|Colour of solution|Conductivity Of Solution|Ionic Or Molecular|
+|:-------|:------------------------|:------------------|:-----------------|:-----------------------|:-----------------|
+|ammonium chloride|solid|soluble, overtime the substance starts to get smaller and disappears|colourless|conductive|ionic|
+|copper $`(II)`$ sulfate|solid|soluable|blue|conductive|ionic|
+|sodium chloride|solid|soluble|colourless|conductive|ionic|
+|calcium hydroxide|solid|slightly soluable|white|slightly conductive|ionic|
+|sodium hydroxide|solid|soluble|colourless|conductive|ionic|
+|sucrose|solid|soluble|colourless|not conductive|molecular|
+|iodine|solid|not soluble|yellow|not conductive|molecular|
+|hydrochloric acid|aqueous|soluble|colourless|conductive|molecular|
+|ethanol|liquid|soluble|colourless|nont conductive|molecular|
+|nitrogen gas|gas|N/A|N/A|N/A|molecular|
+|carbon dioxide (dissolved in water)|gas|slightly soluble|colourless|a tiny bit conductive|molecular|
+
+## Generalizations
+|Classification of substances|Phase at room temperature|Solubility in water|Colour of solution|Conductivity of solution|
+|:---------------------------|:------------------------|:------------------|:-----------------|:-----------------------|
+|Ionic|Solid|Soluble|colourless, white|Conductive|
+|Molecualr|liquid, gas, or solid|non-soluble|Has distinct colour?|Not really conductive|
+
+## Binary Molecular Compounds
+|Chemical Formula|Lewis Structure|What does the molecular model look like?|Name|
+|:---------------|:-------------:|:--------------------------------------:|:---|
+|$`H_2`$|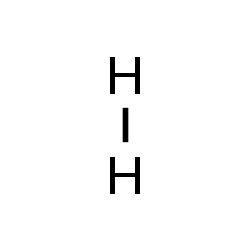 |
| |Hydrogen|
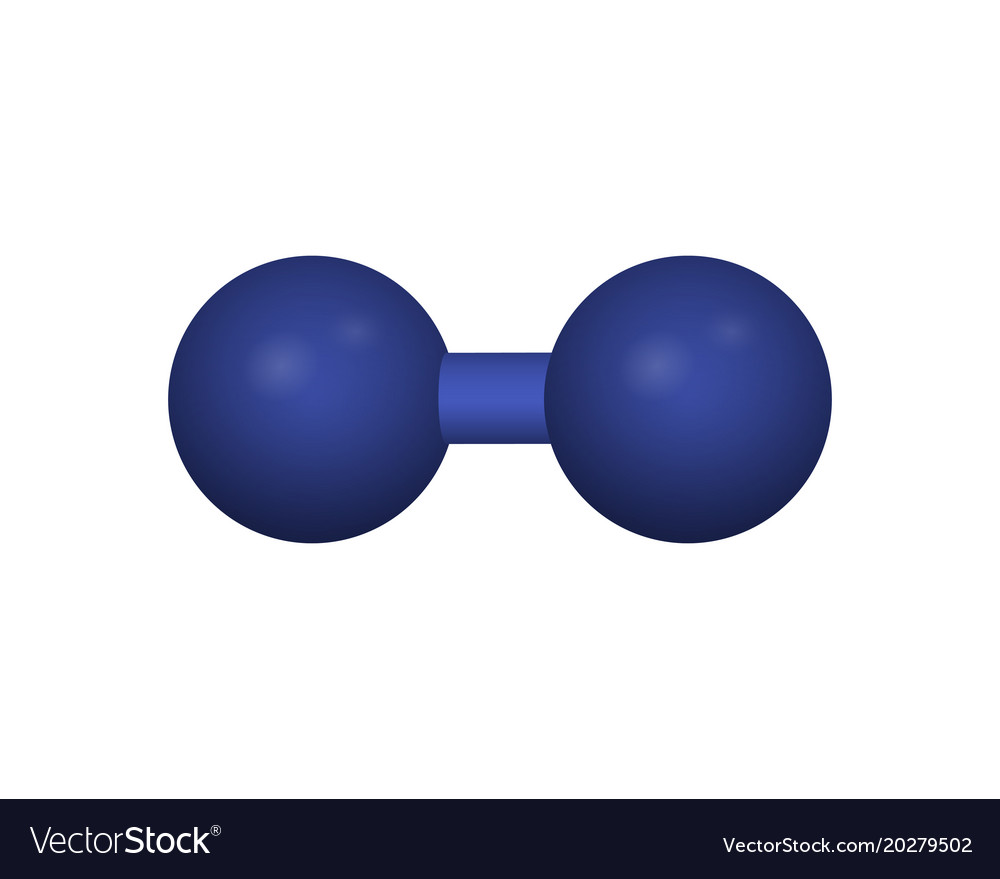
+|$`O_2`$|
|Hydrogen|
+|$`O_2`$|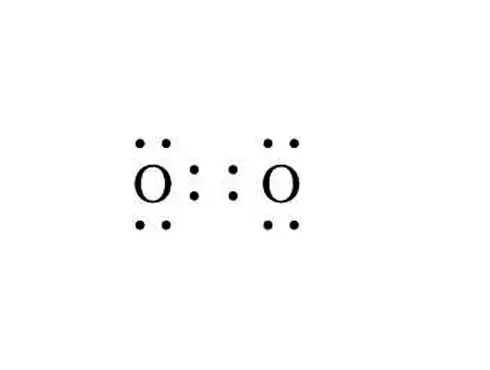 |
| |Oxygen|
+|$`N_2`$|
|Oxygen|
+|$`N_2`$| |
| |Nitrogen|
+|$`I_2`$|
|Nitrogen|
+|$`I_2`$| |
| |Iodine|
+|$`H_2O`$|
|Iodine|
+|$`H_2O`$| |
| |Water|
|Water|
 |Hydrogen|
+|$`O_2`$|
|Hydrogen|
+|$`O_2`$| |
| |Oxygen|
+|$`N_2`$|
|Oxygen|
+|$`N_2`$| |
| |Nitrogen|
+|$`I_2`$|
|Nitrogen|
+|$`I_2`$| |
| |Iodine|
+|$`H_2O`$|
|Iodine|
+|$`H_2O`$| |
| |Water|
|Water|