diff --git a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
index 4bb7789..5825486 100644
--- a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
+++ b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
@@ -105,6 +105,41 @@
| Chemical Change |
A change in the starting substance and the production of ONE or more new substances
Original substance does not disappear BUT the composition is rearranged |
+
+| Molecule |
+Two or more non-metal atoms joined together |
+
+
+| Diatomic Molecules |
+Molecules that only consists of 2 elements
`H O F BR I N CL` - `hyrodgen`, `oxygen`, `fluorine`, `bromine`, `iodine`, `nitrogen`, `chlorine`. |
+
+
+| Ions |
+A Charged particle, that results from a loss (cation - positve, less electrons) or gain (anion - negative, more electrons) of electrons when bonding |
+
+
+| Electron |
+Negatively Charged |
+
+
+| Proton |
+Positively Charged |
+
+
+| Neutron |
+Neutral Charged |
+
+Ionic Charge |
+The sum of the positive and negative charges in a ion |
+
+
+| Covalent Bond |
+The sharing of electrons between atoms when bonding |
+
+
+| Valence Electrons |
+Number of electrons on the most outer orbit/shell of the element |
+
## Particle Theory of Matter
@@ -211,8 +246,37 @@
## Carbon
## Atoms
+- Subscripts - tells us how many of the atom are there, for example N2 means there are 2 nitrongen atoms.
+- Use distrubutive property if there are brackets and a subscript, for example, (CO)2 is equilivant to C2O2.
+- Atoms are stable if they have a full valence shell (noble gases)
+- Each family has the same amount of valence electrons as their family number, so `alkali metals` would have 1 valence electron, `alkaline earth metals` will have 2, `halogens will have` 7 and `noble gases` would have 8.
+- They will also have the same amount of protons as their `atomic number`.
+- **Number of protons = Number of electrons**.
+- **Number of neutrons = mass - atomic number/number of protons**.
+
+
+## Bohr-Rutherford / Lewis-Dot Diagrams
+- **Bohr-Rutherford**
+ - Draw nucleus, and draw the apprioate number of orbits.
+ - Put number of **protons** and **neutrons** in the nucleus.
+ - Draw the correct number of electrons in each orbit
+  +
+- **Lewis-Dot Diagrams**
+ - Draw element symbol
+ - Put the right number of valence electrons around the symbol, perferably in pairs
+
+
+- **Lewis-Dot Diagrams**
+ - Draw element symbol
+ - Put the right number of valence electrons around the symbol, perferably in pairs
+  +
+### Bonding
+- To combine 2 atoms, each element wants to be stable. So they each want a full valence shell, (outer shell) so they are stable.
+- They can either `gain`, `lose` or `share` electrons in order to become stable.
+- Example:
+ - Oxygen and Hydrogen, in order to become stable, they all need 8 valence electrons. Hydrogen has 1, oxygen has 6, so we bring in another hyrdogen and we let them share all their electrons, turning into H2O, or water.
+
+
+### Bonding
+- To combine 2 atoms, each element wants to be stable. So they each want a full valence shell, (outer shell) so they are stable.
+- They can either `gain`, `lose` or `share` electrons in order to become stable.
+- Example:
+ - Oxygen and Hydrogen, in order to become stable, they all need 8 valence electrons. Hydrogen has 1, oxygen has 6, so we bring in another hyrdogen and we let them share all their electrons, turning into H2O, or water.
+ 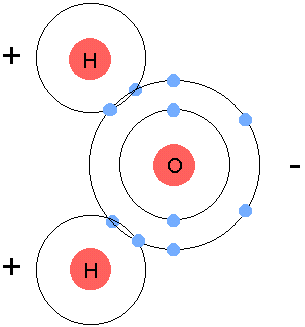 +
+- Use **arrows** to show gaining or losing electrons.
+- **Circle** to show sharing of electrons.
-## Bohr-Rutherford / Louis-Dot Diagrams
## Naming of Ionic Bonds
+
+- Use **arrows** to show gaining or losing electrons.
+- **Circle** to show sharing of electrons.
-## Bohr-Rutherford / Louis-Dot Diagrams
## Naming of Ionic Bonds
 +
+- **Lewis-Dot Diagrams**
+ - Draw element symbol
+ - Put the right number of valence electrons around the symbol, perferably in pairs
+
+
+- **Lewis-Dot Diagrams**
+ - Draw element symbol
+ - Put the right number of valence electrons around the symbol, perferably in pairs
+  +
+### Bonding
+- To combine 2 atoms, each element wants to be stable. So they each want a full valence shell, (outer shell) so they are stable.
+- They can either `gain`, `lose` or `share` electrons in order to become stable.
+- Example:
+ - Oxygen and Hydrogen, in order to become stable, they all need 8 valence electrons. Hydrogen has 1, oxygen has 6, so we bring in another hyrdogen and we let them share all their electrons, turning into H2O, or water.
+
+
+### Bonding
+- To combine 2 atoms, each element wants to be stable. So they each want a full valence shell, (outer shell) so they are stable.
+- They can either `gain`, `lose` or `share` electrons in order to become stable.
+- Example:
+ - Oxygen and Hydrogen, in order to become stable, they all need 8 valence electrons. Hydrogen has 1, oxygen has 6, so we bring in another hyrdogen and we let them share all their electrons, turning into H2O, or water.
+  +
+- Use **arrows** to show gaining or losing electrons.
+- **Circle** to show sharing of electrons.
-## Bohr-Rutherford / Louis-Dot Diagrams
## Naming of Ionic Bonds
+
+- Use **arrows** to show gaining or losing electrons.
+- **Circle** to show sharing of electrons.
-## Bohr-Rutherford / Louis-Dot Diagrams
## Naming of Ionic Bonds