diff --git a/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 3: Physics.md b/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 3: Physics.md
index 2eb1122..0d0b3b5 100644
--- a/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 3: Physics.md
+++ b/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 3: Physics.md
@@ -33,6 +33,20 @@
- Blacks absorb all visible light while whites do the opposite
### Luminescence
+
+|Type Of Luminescence|Description|Picture|
+|:-------------------|:----------|:------|
+|Incandescence|- Produces light by using high temperature to create heat and light.
- Occurs in light bulbs, where electricity passes through a **filament** using made of tungsten it becomes so hot that it gives off visible light
- It also emits `infrared` light that you feel as heat radiating from the bulb depending on the bulb only a tiny fraction is converted to visible light the rest is converted to `infrared` light.
- This is makes this process very inefficient
- Examples include
- incandescence light bulbs
- burning candle
- lit sparks flying off a grinder| |
+|Electric Discharge|- The process of producing light by passing electric current through a gas. Different gases produce different colours when electricity is passed through
|
+|Electric Discharge|- The process of producing light by passing electric current through a gas. Different gases produce different colours when electricity is passed through
- Examples include:
- Neon light signs
- Lightning (in this case, the gas is air)| |
+|Phosphorescence|- The process of producing light by the absorption of `ultraviolet` light resulting in the emission of visible light over an **extended** period of time
|
+|Phosphorescence|- The process of producing light by the absorption of `ultraviolet` light resulting in the emission of visible light over an **extended** period of time
- This is different than `Fluorescene`, as the light is released over a period of time
- Often described as `glow-in-the-dark` materials
- Examples include:
- glow in the dark watches, stickers, clocks etc| |
+|Fluoresence|- Process of producing light immediately as a result of the absorbtion of `ultraviolet` light
|
+|Fluoresence|- Process of producing light immediately as a result of the absorbtion of `ultraviolet` light
- Detergent manufacturerse often add flourescent dyes to make washed shirts more brighter
- This is process is even apparent in visible light because normal daylight includes a small amount of `ultraviolet` light
- Flourescent lights makes use of both `electric discharge` and `fluorescence`. The electric gas (usually mercury) produces ultra-violet light during electric discharge, which is then used to produce visible light.
- Fluorescent lights 4-5 more efficient than incandescent bulbs
- Examples include:
- Fluorescent lights| |
+|Chemiluminescence|- The direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction with **little** or **no heat** produced
|
+|Chemiluminescence|- The direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction with **little** or **no heat** produced
- Light sticks is glow because when snapped, the 2 chemicals react with each other to produce light.
- Chemiluminescence does not rely on `electric discharge`, little heat produced, no moving parts and can be sealed with durable material, making it very useful in hazardous environments.
- Examples include:
- Light sticks|:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/flasks-with-glowing-liquids-520120820-594044535f9b58d58a548082.jpg) |
+|Bioluminescence|- The production of light in living organisms as the result of `chemiluminescence`
|
+|Bioluminescence|- The production of light in living organisms as the result of `chemiluminescence`
Examples include:
- Fireflies
- fungi
- marine invertebrates
- fish
- glow-worms
- certain bacteria|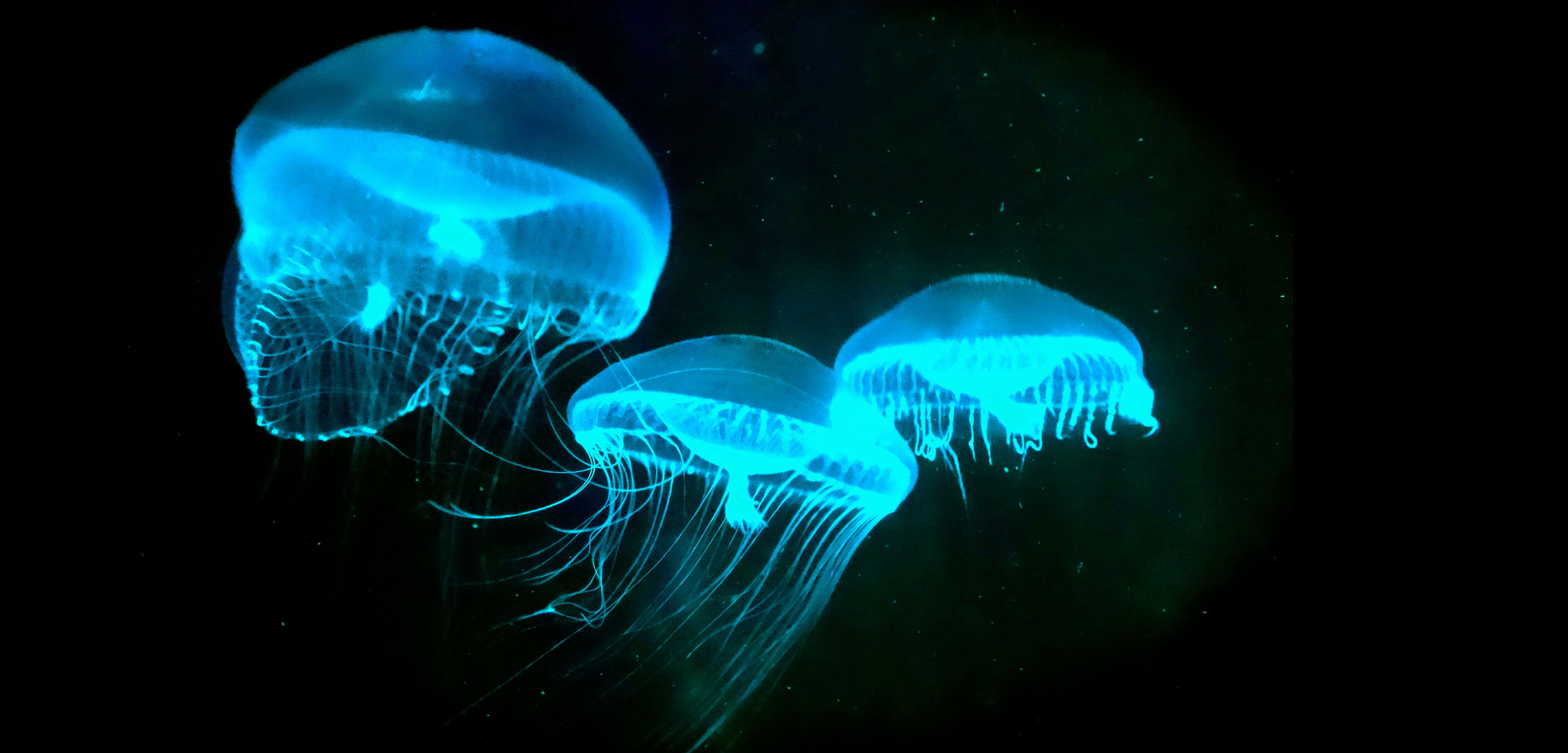 |
+|Triboluminescence|- The production of light from **friction** as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain cystals
|
+|Triboluminescence|- The production of light from **friction** as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain cystals
- Examples include:
- Rubbing twoquartz crystals together will produce light due to triboluminescence| |
+|Light-Emitting Diode (LED)|- light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in **semiconductors**.
|
+|Light-Emitting Diode (LED)|- light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in **semiconductors**.
- **semiconductors** are materials that allow an electric current to flow in only one direction
- When electricity flows in the allowed direction, the LEd emits light
- **Does not** produce much **heat** as a by-product, nor require a **filament**, and is more energy efficient
- Examples include
- LED lights
- christmas tree lights
- illuminated signs
- traffic lights|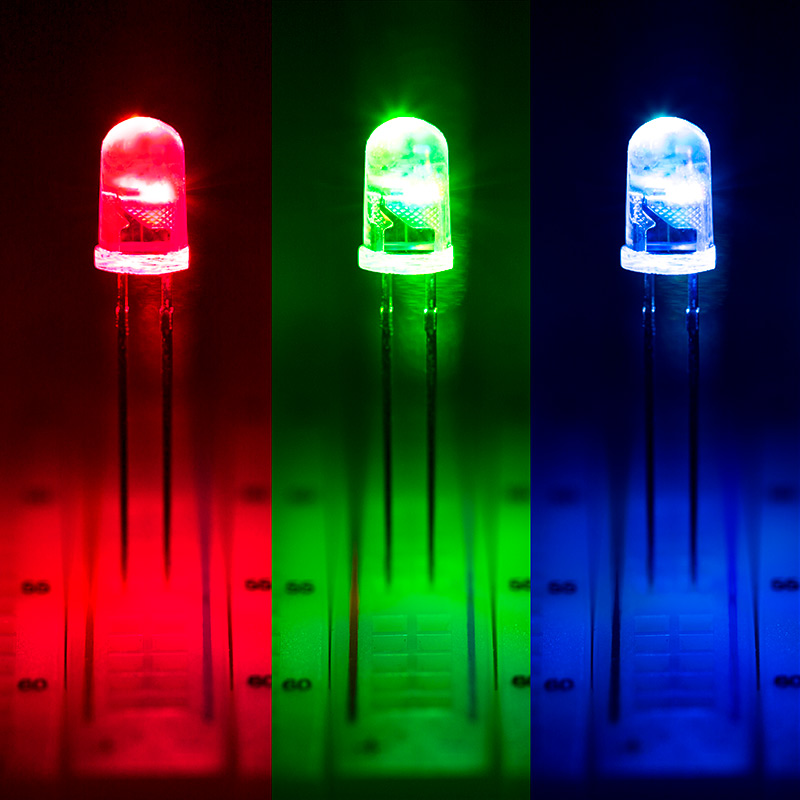 |
+
+
+
- Things that emit light fill in here plz thanks
### Rays
|
+
+
+
- Things that emit light fill in here plz thanks
### Rays
 |
+|Electric Discharge|- The process of producing light by passing electric current through a gas. Different gases produce different colours when electricity is passed through
|
+|Electric Discharge|- The process of producing light by passing electric current through a gas. Different gases produce different colours when electricity is passed through |
+|Phosphorescence|- The process of producing light by the absorption of `ultraviolet` light resulting in the emission of visible light over an **extended** period of time
|
+|Phosphorescence|- The process of producing light by the absorption of `ultraviolet` light resulting in the emission of visible light over an **extended** period of time |
+|Fluoresence|- Process of producing light immediately as a result of the absorbtion of `ultraviolet` light
|
+|Fluoresence|- Process of producing light immediately as a result of the absorbtion of `ultraviolet` light |
+|Chemiluminescence|- The direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction with **little** or **no heat** produced
|
+|Chemiluminescence|- The direct production of light as the result of a chemical reaction with **little** or **no heat** produced:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/flasks-with-glowing-liquids-520120820-594044535f9b58d58a548082.jpg) |
+|Bioluminescence|- The production of light in living organisms as the result of `chemiluminescence`
|
+|Bioluminescence|- The production of light in living organisms as the result of `chemiluminescence` |
+|Triboluminescence|- The production of light from **friction** as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain cystals
|
+|Triboluminescence|- The production of light from **friction** as a result of scratching, crushing, or rubbing certain cystals |
+|Light-Emitting Diode (LED)|- light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in **semiconductors**.
|
+|Light-Emitting Diode (LED)|- light produced as a result of an electric current flowing in **semiconductors**.  |
+
+
+
- Things that emit light fill in here plz thanks
### Rays
|
+
+
+
- Things that emit light fill in here plz thanks
### Rays