diff --git a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
index 7494d9c..bec8725 100644
--- a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
+++ b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
@@ -426,6 +426,13 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
- Erosion and sedimentation
+### Human Inpacts
+- Humans building dams (flooding is a problem!)
+- Deforestation contributes to global warming, hence melting glaciers and causing flooding in cities
+- (Also less transpiration from clear cutting) – pg. 48
+- Factories and cars pollute the air, leading to acid precipitation
+- Oil spills destroy aquatic ecosystems
+
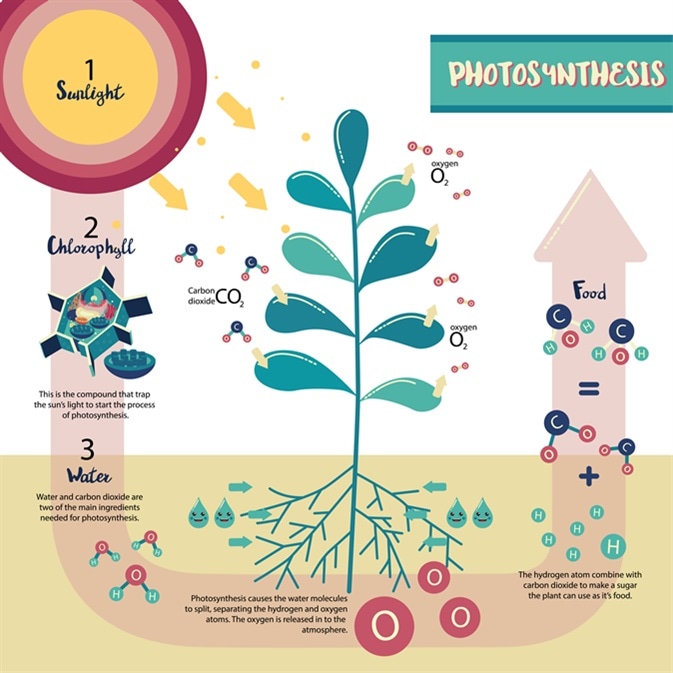
## Carbon Cycle
- Fourth most abundant element in universe
- Building block of all living things
@@ -436,8 +443,23 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
+- Carbon dioxide is `returned to the enviornment by:
+ 1. `Resipiration` in plants, animals & micro-organisms.
+ 2. `Decay` caused by micro-organisms (decompoers).
+ 3. `Combustion` i.e. Burning fossil fuels.
+- **Phtosynthesis**
+ - CO2 is converted to glucose using water and sunlight
+- **Cellular Respiration**
+ - Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
+- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
-  +### Human Impacts
+- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
+- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
+- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
+- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
+
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
@@ -446,8 +468,10 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+
+
### STEPS/PROCESSES
--
+### Human Impacts
+- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
+- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
+- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
+- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
+
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
@@ -446,8 +468,10 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+
+
### STEPS/PROCESSES
-- 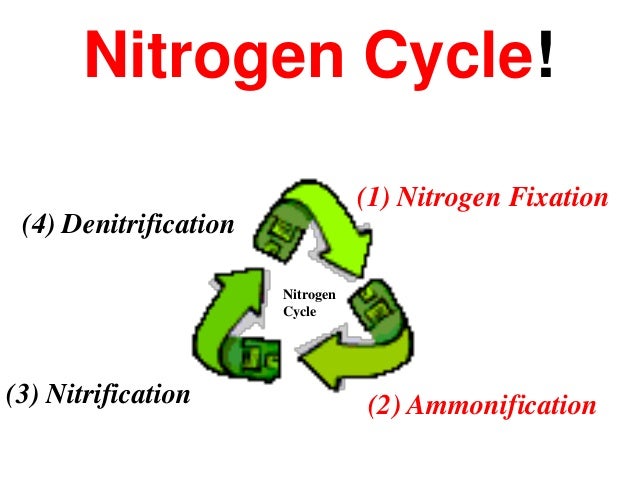 +-
+-  ### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -456,6 +480,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
+ - Lightning Storms
+ - stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
@@ -464,7 +490,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
-
+- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
+- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
+- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
+ - This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
+
+### Human Impacts
+- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
+- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Nutrient Recycling
- There is a `limited` amount of `nutrients` on earth
@@ -473,7 +506,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- There are similar cycles for all nutrients.
- When plants and animals die, their nutrient content is `not wasted`.
- Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment (i.e. into the soil, nearby water and air).
+- Nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material.
+- This material is passed on down the food chains and is reused by all the chain members.
+- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
+- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
+### Summary Of Nutrient Recycling
+- The way in which elements are continuously being broken down and/or exchanged for reuse
+- Occurs between the living and non-living components of an ecosystem.
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -456,6 +480,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
+ - Lightning Storms
+ - stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
@@ -464,7 +490,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
-
+- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
+- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
+- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
+ - This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
+
+### Human Impacts
+- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
+- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Nutrient Recycling
- There is a `limited` amount of `nutrients` on earth
@@ -473,7 +506,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- There are similar cycles for all nutrients.
- When plants and animals die, their nutrient content is `not wasted`.
- Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment (i.e. into the soil, nearby water and air).
+- Nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material.
+- This material is passed on down the food chains and is reused by all the chain members.
+- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
+- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
+### Summary Of Nutrient Recycling
+- The way in which elements are continuously being broken down and/or exchanged for reuse
+- Occurs between the living and non-living components of an ecosystem.
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
 +### Human Impacts
+- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
+- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
+- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
+- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
+
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
@@ -446,8 +468,10 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+
+
### STEPS/PROCESSES
--
+### Human Impacts
+- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
+- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
+- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
+- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
+
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
@@ -446,8 +468,10 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+
+
### STEPS/PROCESSES
--  +-
+-  ### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -456,6 +480,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
+ - Lightning Storms
+ - stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
@@ -464,7 +490,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
-
+- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
+- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
+- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
+ - This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
+
+### Human Impacts
+- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
+- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Nutrient Recycling
- There is a `limited` amount of `nutrients` on earth
@@ -473,7 +506,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- There are similar cycles for all nutrients.
- When plants and animals die, their nutrient content is `not wasted`.
- Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment (i.e. into the soil, nearby water and air).
+- Nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material.
+- This material is passed on down the food chains and is reused by all the chain members.
+- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
+- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
+### Summary Of Nutrient Recycling
+- The way in which elements are continuously being broken down and/or exchanged for reuse
+- Occurs between the living and non-living components of an ecosystem.
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -456,6 +480,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
+ - Lightning Storms
+ - stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
@@ -464,7 +490,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
-
+- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
+- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
+- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
+ - This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
+
+### Human Impacts
+- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
+- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Nutrient Recycling
- There is a `limited` amount of `nutrients` on earth
@@ -473,7 +506,14 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- There are similar cycles for all nutrients.
- When plants and animals die, their nutrient content is `not wasted`.
- Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment (i.e. into the soil, nearby water and air).
+- Nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material.
+- This material is passed on down the food chains and is reused by all the chain members.
+- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
+- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
+### Summary Of Nutrient Recycling
+- The way in which elements are continuously being broken down and/or exchanged for reuse
+- Occurs between the living and non-living components of an ecosystem.
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.