- Metals are shiny(lustre)
- Metals are ductile (can be stretched into thin wires
- Metals are malleable (can be pounded into thin sheets)
- A chemical property of metal is its reaction with water which reults in corrosion|
 |
-|Non-Metals|- Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity
|
-|Non-Metals|- Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity- Non-metal are **not** `ductile` or `malleable`
- Solid non-metals are `brittle` and break-easily
- They are `dull`
- Many non-metals are gases (one is liquid|
 |
+|Non-Metals|- Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity
|
+|Non-Metals|- Non-metals are poor conductors of heat and electricity- Non-metal are **not** `ductile` or `malleable`
- Solid non-metals are `brittle` and break-easily
- They are `dull`
- Many non-metals are gases (one is liquid)|
 |
|Metalloids|- Metalloids (metal-like) have properties of both metals and non-metals
|
|Metalloids|- Metalloids (metal-like) have properties of both metals and non-metals- They are solids that can be `shiny` or `dull`
- They `conduct` heat and electricity better than non-metals but not as well as metals
- They are `ductile` and `malleable`|
Atoms are never **created or destroyed**.
- Atoms of an element are identical|
- Negatively charged electrons were **evenly distrubuted** throughout the atom.
- **Ray cathode experiment** - basically atoms were attracted to a postive end of the tube, so there most be negative charges in the atoms.
 |
| |
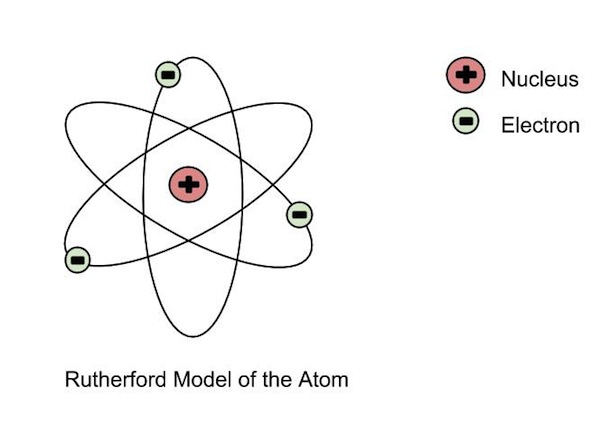
|Ernest Rutherford|- Discovered that the postively charged **nucleus**.
|
|Ernest Rutherford|- Discovered that the postively charged **nucleus**. - The nucleus was **surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons**
- Most of the atom was just space.
- **Gold foil experiement**, alpha particles (postively charged) shot at atom, some bounced off at weird angles, so there most be a postively charged thing there.
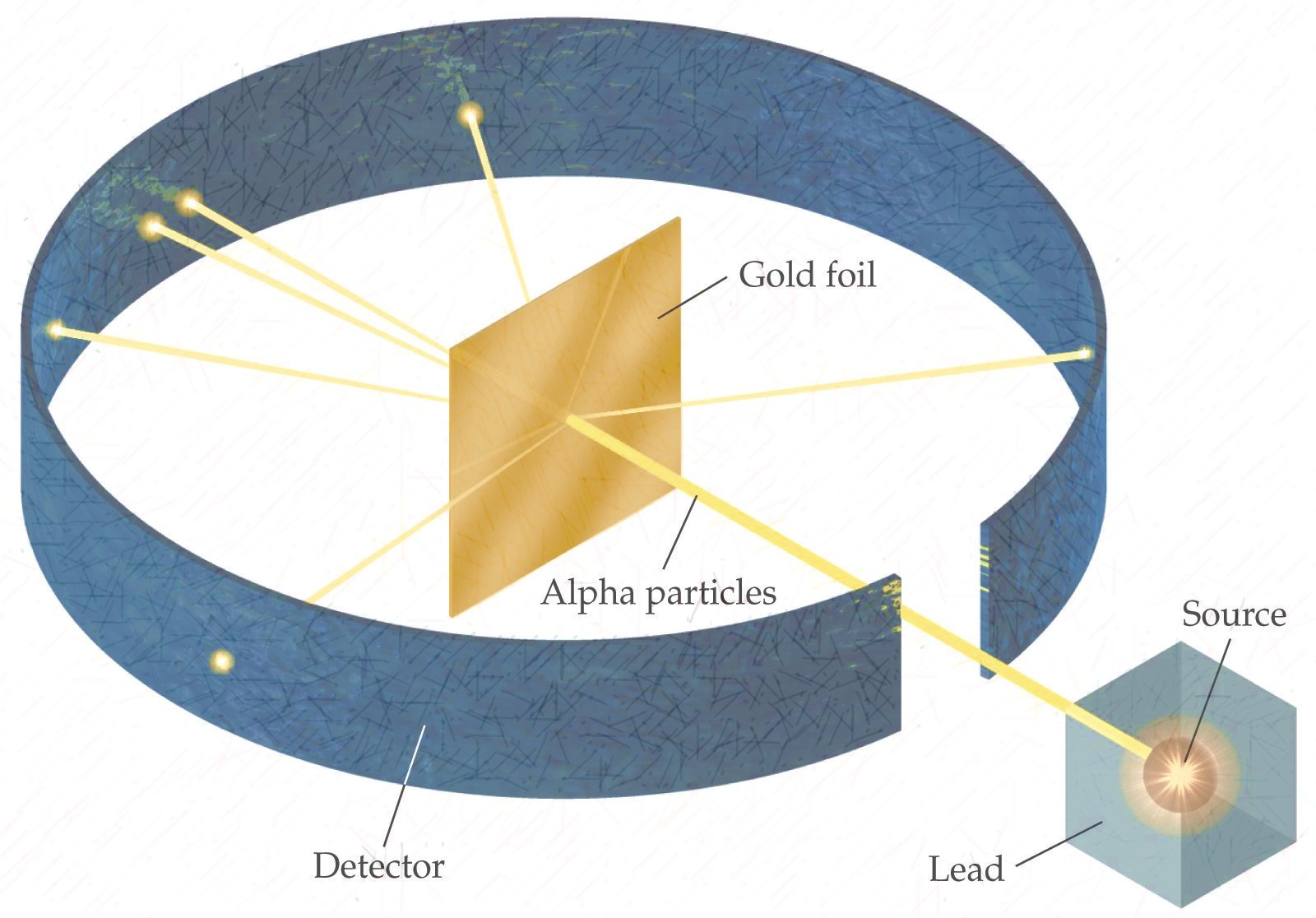 |
| |
-|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucles = more energy.
|
-|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucles = more energy.- Electrons **cannot** jump orbit to orbit or release energy as light going down.
- Each orbit can hold a specifc amount of electrons, `2,8,8,2`, useful for the first 20 elements|
 |
+|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucleus = more energy.
|
+|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucleus = more energy.- Electrons **cannot** jump orbit to orbit or release energy as light going down.
- Each orbit can hold a specifc amount of electrons, `2,8,8,8`, useful for the first 20 elements|
 |
|James Chadwick|- Discovered the neutron, mass of neutron = mass of proton (basically)
|
|James Chadwick|- Discovered the neutron, mass of neutron = mass of proton (basically)- Neutral atoms have **equal numbers** of protons and electrons.|
 |
|