diff --git a/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 2: Biology.md b/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 2: Biology.md
index d0fea66..d795523 100644
--- a/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 2: Biology.md
+++ b/Grade 10/Science/SNC2DZ/Unit 2: Biology.md
@@ -178,6 +178,9 @@ A person contains roughly 100 trillion cells
- e.g., red blood cells, hair cells, skin, injuries, broken bones
### Cell cycle
+
+ +
- **Interphase**
- Large majority of a cell's time is spent in interphase
- **G1**: (normal growth and function),
@@ -207,10 +210,10 @@ A person contains roughly 100 trillion cells
| Phase | Diagram | Description |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
-| Prophase | | - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`
+
- **Interphase**
- Large majority of a cell's time is spent in interphase
- **G1**: (normal growth and function),
@@ -207,10 +210,10 @@ A person contains roughly 100 trillion cells
| Phase | Diagram | Description |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
-| Prophase | | - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`
- Happens to 23 pairs of chromosomes
- Nuclear membrane dissolves
- Centrosomes move to opposite ends (`poles`) of cell, creating `spindle fibres` that begin to attach to `centromeres` in animal cells |
-| Metaphase | | - Chromosomes line up in centre of cell to ensure they divide evenly
- Everything in prophase has completed (e.g., nuclear membrane has dissolved completely) |
-| Anaphase | | - Centromeres split, separating sister chromatids
- Sister chromatids are pulled towards opposite sides of cell via shortening spindle fibres
- Sister chromatids are now called `daughter chromomsomes` |
-| Telophase | | - Effectively opposite of prophase
- Nuclear membranes form across each of the two new nuclei
- Daughter chromosomes unwind into chromatin and are no longer visible
- Nucleolus forms in each nucleus
- Spindle fibres break apart
- **Cytokinesis** usually begins in telophase
- Cells starts to **cleave** (cell centre starts to pinch itself) |
+| Prophase | 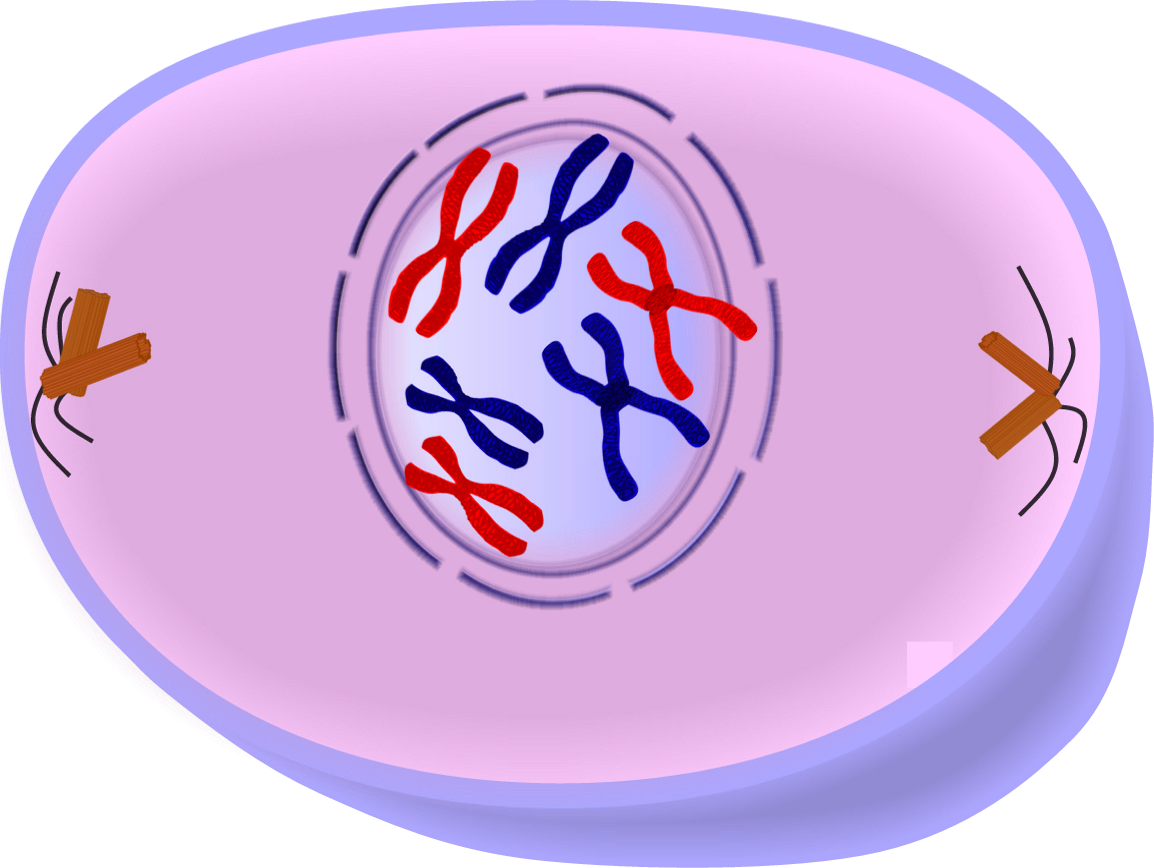 | - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`
| - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`
- Happens to 23 pairs of chromosomes
- Nuclear membrane dissolves
- Centrosomes move to opposite ends (`poles`) of cell, creating `spindle fibres` that begin to attach to `centromeres` in animal cells |
+| Metaphase | 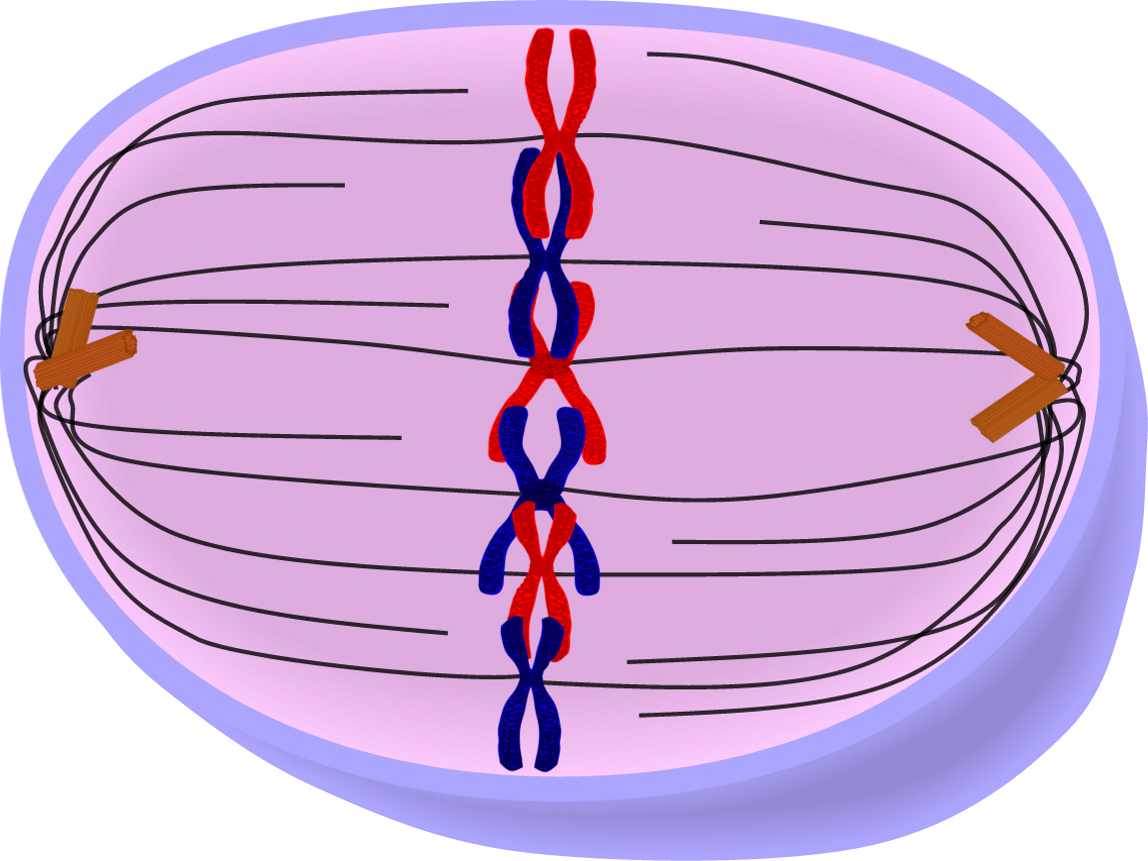 | - Chromosomes line up in centre of cell to ensure they divide evenly
| - Chromosomes line up in centre of cell to ensure they divide evenly
- Everything in prophase has completed (e.g., nuclear membrane has dissolved completely) |
+| Anaphase | 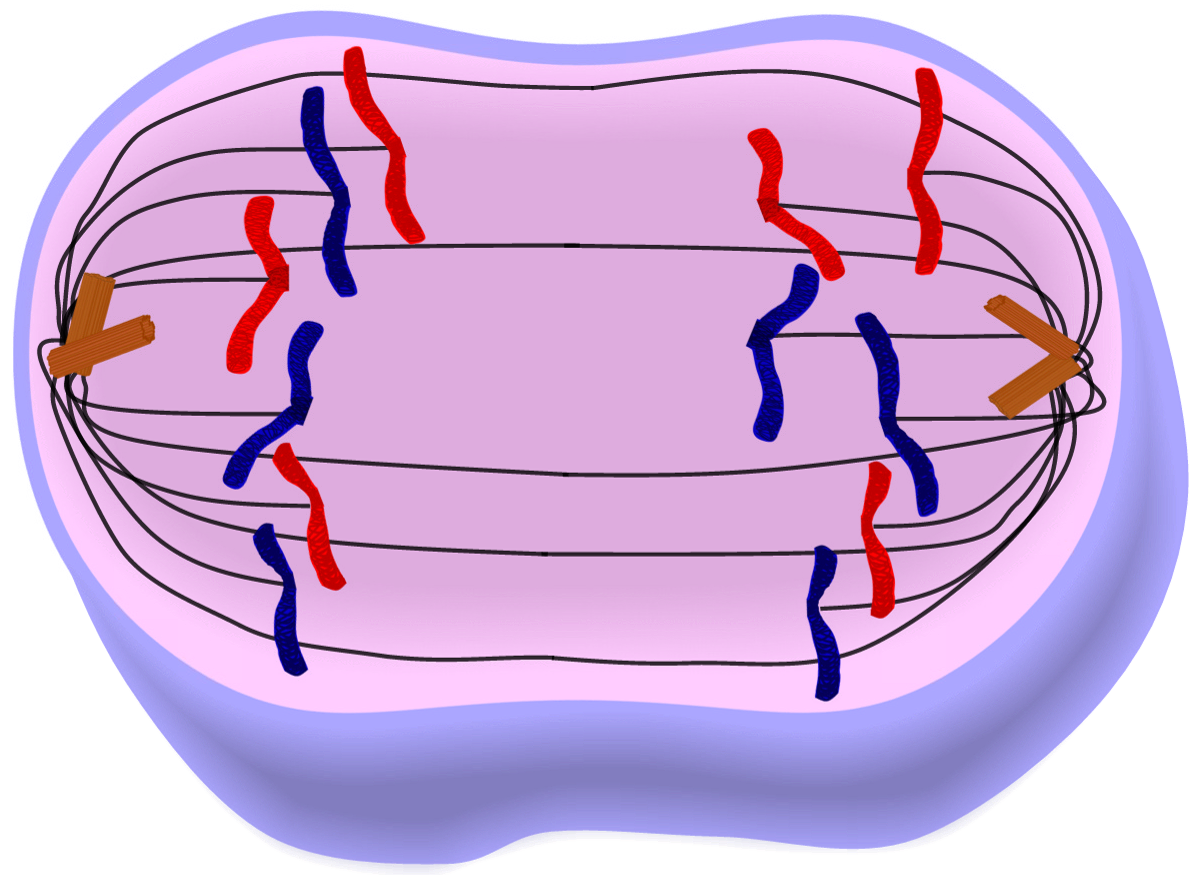 | - Centromeres split, separating sister chromatids
| - Centromeres split, separating sister chromatids
- Sister chromatids are pulled towards opposite sides of cell via shortening spindle fibres
- Sister chromatids are now called `daughter chromomsomes` |
+| Telophase | 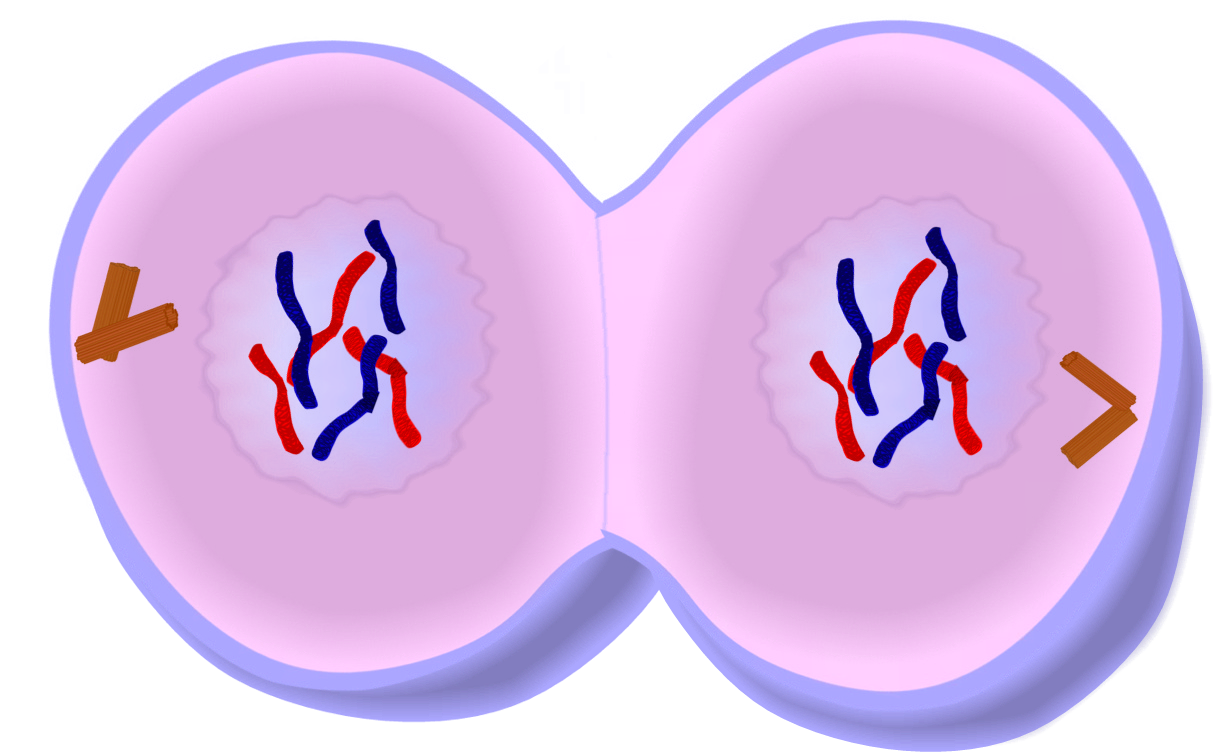 | - Effectively opposite of prophase
| - Effectively opposite of prophase
- Nuclear membranes form across each of the two new nuclei
- Daughter chromosomes unwind into chromatin and are no longer visible
- Nucleolus forms in each nucleus
- Spindle fibres break apart
- **Cytokinesis** usually begins in telophase
- Cells starts to **cleave** (cell centre starts to pinch itself) |
### Cytokinesis
- Cell division
 +
- **Interphase**
- Large majority of a cell's time is spent in interphase
- **G1**: (normal growth and function),
@@ -207,10 +210,10 @@ A person contains roughly 100 trillion cells
| Phase | Diagram | Description |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
-| Prophase | | - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`
+
- **Interphase**
- Large majority of a cell's time is spent in interphase
- **G1**: (normal growth and function),
@@ -207,10 +210,10 @@ A person contains roughly 100 trillion cells
| Phase | Diagram | Description |
| :--- | :--- | :--- |
-| Prophase | | - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`  | - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`
| - Chromatin condenses into two identical `sister chromatids` which condense into `chromosomes`  | - Chromosomes line up in centre of cell to ensure they divide evenly
| - Chromosomes line up in centre of cell to ensure they divide evenly  | - Centromeres split, separating sister chromatids
| - Centromeres split, separating sister chromatids  | - Effectively opposite of prophase
| - Effectively opposite of prophase