(size of an atom)
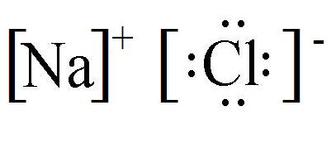 +
## Non-Metal Ionic Names
|Element|Name|
@@ -131,6 +163,8 @@
- Naming and writing chemical formuals
- According to IUPAC
- Direct relationship beween chemical name and chemical structure
+- - Going down diagonally from `aluminium`, we get a pattern of $`3+`$, $`2+`$, $`1+`$ of charge. `Aluminium` has a charge of $`3+`$, `Zinc` has a charge of $`2+`$, and `silver` has a charge of $`1+`$, and they are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
+ - `Galvanize` (rust $`\rightarrow`$ white shield $`\rightarrow`$ cover iron $`\rightarrow`$ prevnet rusting, but I don't think it will be in this unit)
|Formula|Name|
|:------|:---|
@@ -152,10 +186,7 @@
- non-metals (the ones hugging the staircase are also non-metals (some of the `metalloids`))
- `halogens`
- `noble gases`
-
-- Going down diagonally from aluminium, we get a pattern of $`3+`$, $`2+`$, $`1+`$ of charge. Aluminium has a charge of $`3+`$, Zinc has a charge of $`2+`$, and silver has a charge of $`1+`$, and they
-are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
-- If there is more than one polyatomic ion in a formula unit, then surround the ion with brackets
+- If there is more than one polyatomic ion in a formula unit, then surround the ion with brackets/parentheses
- Oxyanion are negative ions with oxygen in them
|Polyatomic Ion Name|Formula (Always Remember The Charge!)|
@@ -174,6 +205,15 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|Sulfate|$`SO_4^{2-}`$|
|Phosphate|$`PO_4^{3-}`$|
+### Oxyanions
+- Nitrate
+- Borate
+- Carbonate
+- Chlorate
+- Sulfate
+- Phosphate
+- And their family members :p.
+
## Deriving Ions From Parent
|Polyatomic Ion Name|Operation|Chemical Formula|
@@ -191,6 +231,8 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|Bromate|$`BrO_3^-`$|
## Acidic Oxyanions
+- Acids generall have hydrogen ions $`(H^+)`$
+- Acidic Oxyanions $`\rightarrow`$ Negatively charged ion with $`O`$ and $`H`$
- Each hydrogen added to a polyatomic ion increases the charge by one, and changes the name:
|Name|Chemical Formula|
@@ -199,15 +241,14 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|Dihydrogen phosphate ion|$`H2PO_4^-`$|
|Monohydrogen phosphate ion|$`HPO_4^{2-}`$|
-- For above, we use mono for phosphate to avoid ambigious cases, where $`H_2PO_4^{-}`$ and $`H_2PO_4^{2-}`$ are the same if we don't put `mono` infront. As for the Hyrogen carbonate ion
-we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
+- For above, we use mono for phosphate to avoid ambigious cases, where $`H_2PO_4^{-}`$ and $`H_2PO_4^{2-}`$ are the same if we don't put `mono` infront. As for the Hyrogen carbonate ion we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
## Molecular Compounds
- Are not made of ions, instead molecules
- Shared pair of electrons -> `covalent bonds`
-- Lone pair of electrons are electrons that are not shared
-- Radicals are unpaired electrons, vefy reactive
-- Molecules have no charge
+- `Lone pair` of electrons are electrons that are not shared
+- Radicals are atoms with unpaired electrons, very reactive
+- Molecules have **no charge**
- Atoms fill their valence shells to form molecules
- Double bond between oxygen atoms in an oxygen molecule
@@ -233,6 +274,29 @@ we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
|Molecualr|liquid, gas, or solid|non-soluble|Has distinct colour?|Not really conductive|
## Binary Molecular Compounds
+- 2 different kinds of atom in molecule
+ - Eg. $`CO_2 \rightarrow`$ Carbon Diox**ide** $`\rightarrow`$ 2nd atom has `ide`.
+ - $`CO \rightarrow`$ Carbon Monox**ide** $`\rightarrow`$ If 1st atom is mono, drop `mono`
+
+### Greek Prefix For Number Of Atom
+|Prefix|Name|Preifx|Name|
+|:-----|:---|:-----|:---|
+|1|mono|6|hexa|
+|2|di|7|hepta|
+|3|tri|8|octa|
+|4|tetra|9|nona|
+|5|penta|10|deca|
+
+- `Diatomic Molecules` The **gens**, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Halogen
+
+### Common Names
+- $`NH_3 \rightarrow`$ Ammonia
+- $`H_2O \rightarrow`$ Water
+- $`CH_4 \rightarrow`$ Methane
+
+### Elements found As Molecules In Nature
+- $`H_{2(g)}, Cl_{2(g)}, Br_{2(g)}, I_2, N_2, O_2, F_2`$
+
|Chemical Formula|Lewis Structure|What does the molecular model look like?|Name|
|:---------------|:-------------:|:--------------------------------------:|:---|
|$`H_2`$|
+
## Non-Metal Ionic Names
|Element|Name|
@@ -131,6 +163,8 @@
- Naming and writing chemical formuals
- According to IUPAC
- Direct relationship beween chemical name and chemical structure
+- - Going down diagonally from `aluminium`, we get a pattern of $`3+`$, $`2+`$, $`1+`$ of charge. `Aluminium` has a charge of $`3+`$, `Zinc` has a charge of $`2+`$, and `silver` has a charge of $`1+`$, and they are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
+ - `Galvanize` (rust $`\rightarrow`$ white shield $`\rightarrow`$ cover iron $`\rightarrow`$ prevnet rusting, but I don't think it will be in this unit)
|Formula|Name|
|:------|:---|
@@ -152,10 +186,7 @@
- non-metals (the ones hugging the staircase are also non-metals (some of the `metalloids`))
- `halogens`
- `noble gases`
-
-- Going down diagonally from aluminium, we get a pattern of $`3+`$, $`2+`$, $`1+`$ of charge. Aluminium has a charge of $`3+`$, Zinc has a charge of $`2+`$, and silver has a charge of $`1+`$, and they
-are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
-- If there is more than one polyatomic ion in a formula unit, then surround the ion with brackets
+- If there is more than one polyatomic ion in a formula unit, then surround the ion with brackets/parentheses
- Oxyanion are negative ions with oxygen in them
|Polyatomic Ion Name|Formula (Always Remember The Charge!)|
@@ -174,6 +205,15 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|Sulfate|$`SO_4^{2-}`$|
|Phosphate|$`PO_4^{3-}`$|
+### Oxyanions
+- Nitrate
+- Borate
+- Carbonate
+- Chlorate
+- Sulfate
+- Phosphate
+- And their family members :p.
+
## Deriving Ions From Parent
|Polyatomic Ion Name|Operation|Chemical Formula|
@@ -191,6 +231,8 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|Bromate|$`BrO_3^-`$|
## Acidic Oxyanions
+- Acids generall have hydrogen ions $`(H^+)`$
+- Acidic Oxyanions $`\rightarrow`$ Negatively charged ion with $`O`$ and $`H`$
- Each hydrogen added to a polyatomic ion increases the charge by one, and changes the name:
|Name|Chemical Formula|
@@ -199,15 +241,14 @@ are all mono-valent. (not multi-valent)
|Dihydrogen phosphate ion|$`H2PO_4^-`$|
|Monohydrogen phosphate ion|$`HPO_4^{2-}`$|
-- For above, we use mono for phosphate to avoid ambigious cases, where $`H_2PO_4^{-}`$ and $`H_2PO_4^{2-}`$ are the same if we don't put `mono` infront. As for the Hyrogen carbonate ion
-we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
+- For above, we use mono for phosphate to avoid ambigious cases, where $`H_2PO_4^{-}`$ and $`H_2PO_4^{2-}`$ are the same if we don't put `mono` infront. As for the Hyrogen carbonate ion we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
## Molecular Compounds
- Are not made of ions, instead molecules
- Shared pair of electrons -> `covalent bonds`
-- Lone pair of electrons are electrons that are not shared
-- Radicals are unpaired electrons, vefy reactive
-- Molecules have no charge
+- `Lone pair` of electrons are electrons that are not shared
+- Radicals are atoms with unpaired electrons, very reactive
+- Molecules have **no charge**
- Atoms fill their valence shells to form molecules
- Double bond between oxygen atoms in an oxygen molecule
@@ -233,6 +274,29 @@ we don't put a mono due to no ambigious cases.
|Molecualr|liquid, gas, or solid|non-soluble|Has distinct colour?|Not really conductive|
## Binary Molecular Compounds
+- 2 different kinds of atom in molecule
+ - Eg. $`CO_2 \rightarrow`$ Carbon Diox**ide** $`\rightarrow`$ 2nd atom has `ide`.
+ - $`CO \rightarrow`$ Carbon Monox**ide** $`\rightarrow`$ If 1st atom is mono, drop `mono`
+
+### Greek Prefix For Number Of Atom
+|Prefix|Name|Preifx|Name|
+|:-----|:---|:-----|:---|
+|1|mono|6|hexa|
+|2|di|7|hepta|
+|3|tri|8|octa|
+|4|tetra|9|nona|
+|5|penta|10|deca|
+
+- `Diatomic Molecules` The **gens**, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Halogen
+
+### Common Names
+- $`NH_3 \rightarrow`$ Ammonia
+- $`H_2O \rightarrow`$ Water
+- $`CH_4 \rightarrow`$ Methane
+
+### Elements found As Molecules In Nature
+- $`H_{2(g)}, Cl_{2(g)}, Br_{2(g)}, I_2, N_2, O_2, F_2`$
+
|Chemical Formula|Lewis Structure|What does the molecular model look like?|Name|
|:---------------|:-------------:|:--------------------------------------:|:---|
|$`H_2`$|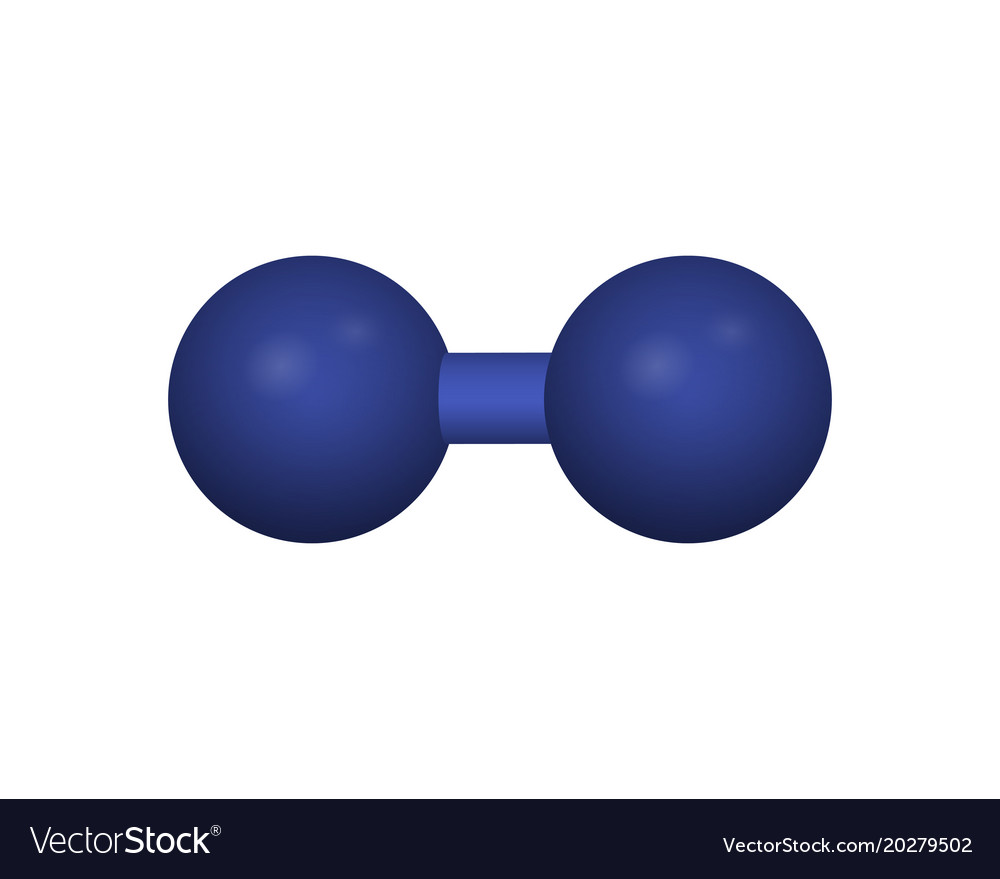 |Hydrogen|
|Hydrogen|
 +
+## Lewis Structures (dot diagrams)
+- shows valence $`e^-`$; centre is atomic symbol
+- Use family groups to figure out valence $`e^-`$
+
+
+
+## Lewis Structures (dot diagrams)
+- shows valence $`e^-`$; centre is atomic symbol
+- Use family groups to figure out valence $`e^-`$
+
+ +
+ ## Trends on the Periodic Table
+- `Periodic Table:` Describes **elements** pure susbatances made of only **1** type of Atom.
+- The further away the electron is from the nucleus, the more energy it has.
+- `Periods:` repeating pattern.
+- Metals on **bottom left**, non-metals on **top right**
+
+### Measuring Atomic Radius
+- Stack a bunch of them, measure, divide by number of atoms, easy clap :p.
## Trends on the Periodic Table
+- `Periodic Table:` Describes **elements** pure susbatances made of only **1** type of Atom.
+- The further away the electron is from the nucleus, the more energy it has.
+- `Periods:` repeating pattern.
+- Metals on **bottom left**, non-metals on **top right**
+
+### Measuring Atomic Radius
+- Stack a bunch of them, measure, divide by number of atoms, easy clap :p.