diff --git a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
index e6dfe91..4bb7789 100644
--- a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
+++ b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
@@ -96,7 +96,15 @@
| Non-Metal |
A substance that isn’t a metal |
-
+
+
+| Physical Change |
+A change in which the composition of the substance remains unaltered` and `no new substances are produced |
+
+
+| Chemical Change |
+A change in the starting substance and the production of ONE or more new substances
Original substance does not disappear BUT the composition is rearranged |
+
## Particle Theory of Matter
@@ -120,7 +128,7 @@
|Qualitative Property|A property that is NOT measured and has **```no numerical value```**|Ex. **```Colour, odor, texture```**|
## Density
-
+ ## Quantitative physical Properties
- **```Density```**: amount of ```stuff``` (or mass) per unit volume (g/cm3)
@@ -147,27 +155,58 @@
- A characteristic (property) of a substance that describes its ability to undergo ```changes to its composition to produce one of more new substances. AKA BEHAVIOUR. Everything has one!```
- ```Cannot be determined by physical properties```
-
- E.g. ability of nails /cars to rust
- Fireworks are explosive
-
- Denim is resistant to soap, but is combustible
-
- Baking soda reacts with vinegar and cake ingredients to rise
-
- Bacterial cultures convert milk to cheese, grapes to wine, cocoa to chocolate
-
- CLR used to clean kettles, showerheads because it breaks down minerals
-
- Silver cleaner for tarnished jewellery, dishes because silver reacts with air to turn black.
-## Physical Change
-
-## Chemical Change
-
## Periodic Table
+
## Quantitative physical Properties
- **```Density```**: amount of ```stuff``` (or mass) per unit volume (g/cm3)
@@ -147,27 +155,58 @@
- A characteristic (property) of a substance that describes its ability to undergo ```changes to its composition to produce one of more new substances. AKA BEHAVIOUR. Everything has one!```
- ```Cannot be determined by physical properties```
-
- E.g. ability of nails /cars to rust
- Fireworks are explosive
-
- Denim is resistant to soap, but is combustible
-
- Baking soda reacts with vinegar and cake ingredients to rise
-
- Bacterial cultures convert milk to cheese, grapes to wine, cocoa to chocolate
-
- CLR used to clean kettles, showerheads because it breaks down minerals
-
- Silver cleaner for tarnished jewellery, dishes because silver reacts with air to turn black.
-## Physical Change
-
-## Chemical Change
-
## Periodic Table
+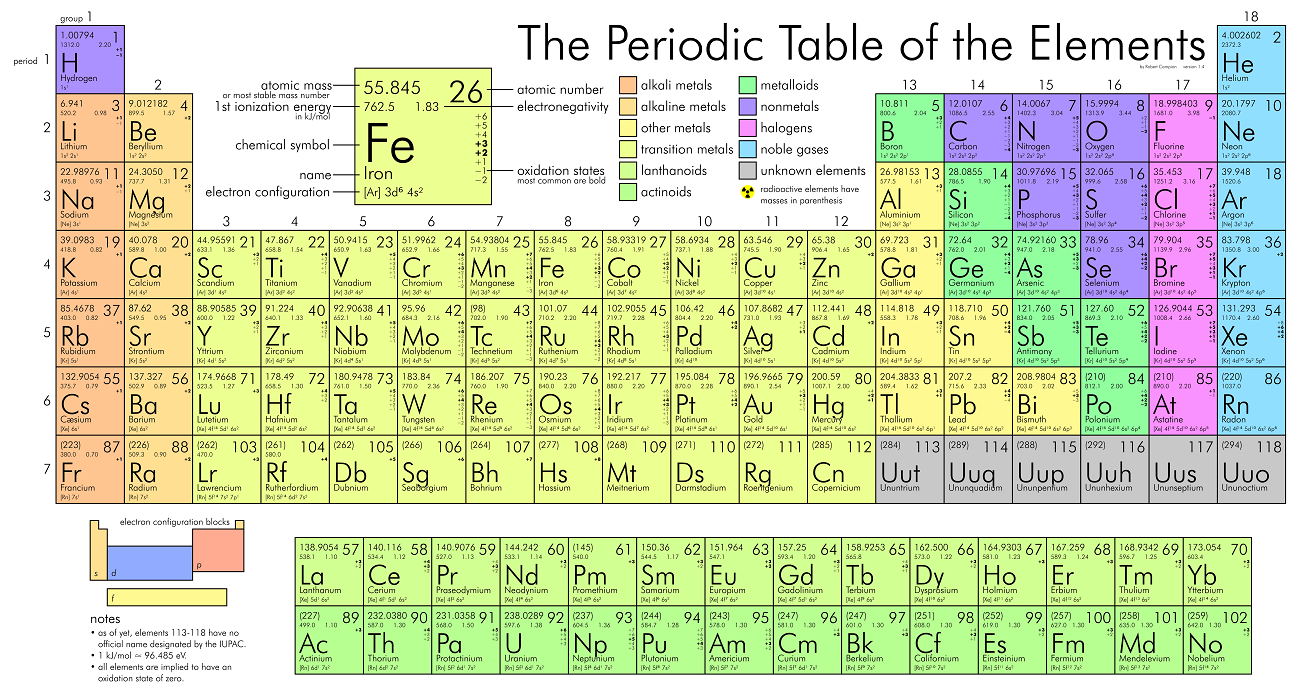 +
+### Trends On The Periodic Table
+- The first column are the `Alkali metals`.
+ - They are shiny, have the consitency of clay, and are easily cut with a knife.
+ - They are the **most reactive** metals.
+ - They react violently with water.
+ - Alkali metals are **never found as free elements in nature**. They are always bonded with another element.
+- The second column are the `Alkaline earth metals`.
+ - They are **never found uncombined in nature**.
+- The last column are the `Noble gases`.
+ - **Extremely un-reactive**.
+- The second last column are the `Halogens`.
+ - The **most reactive non-metals**
+ - They **react with alkali metals to form salts**.
+- The middle parts are the `transition metals`.
+ - They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
+ - Usually bright coloured.
+ - They have properties similar to elements in their same family
+ - Many of them combine with oxygen to form compounds called oxides.
+- The rows outside the table are the `Inner tranistion metals`.
+
+
+
+### Trends On The Periodic Table
+- The first column are the `Alkali metals`.
+ - They are shiny, have the consitency of clay, and are easily cut with a knife.
+ - They are the **most reactive** metals.
+ - They react violently with water.
+ - Alkali metals are **never found as free elements in nature**. They are always bonded with another element.
+- The second column are the `Alkaline earth metals`.
+ - They are **never found uncombined in nature**.
+- The last column are the `Noble gases`.
+ - **Extremely un-reactive**.
+- The second last column are the `Halogens`.
+ - The **most reactive non-metals**
+ - They **react with alkali metals to form salts**.
+- The middle parts are the `transition metals`.
+ - They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
+ - Usually bright coloured.
+ - They have properties similar to elements in their same family
+ - Many of them combine with oxygen to form compounds called oxides.
+- The rows outside the table are the `Inner tranistion metals`.
+
+ +
+- The **left** to the **staircase** are the metals and the **right** are the non-metals. The ones touching the **staircase** are the `metalloids`.
+
+
+
+- The **left** to the **staircase** are the metals and the **right** are the non-metals. The ones touching the **staircase** are the `metalloids`.
+
+ +
+### How To Read An Element
+
+
+### How To Read An Element
+ +
## History of The Atom
+|Person|Description|Picture|
+|:-----|:----------|:------|
+|Democritus|All matter can be divided up into smaller pieces until it reaches an unbreakable particle called an ATOM (cannot be cut)
+
## History of The Atom
+|Person|Description|Picture|
+|:-----|:----------|:------|
+|Democritus|All matter can be divided up into smaller pieces until it reaches an unbreakable particle called an ATOM (cannot be cut)
He proposed atoms are of diffent sizes, in constant motion and separated by empty spaces||
+|Aristole|- Rejected Democritus ideas, believed all matter was made up the 4 elements, it was accepted for nearly 2000 years| |
+|John Dalton|- Billbard model, atoms of **different elements are different**
|
+|John Dalton|- Billbard model, atoms of **different elements are different**
Atoms are never **created or destroyed**.
- Atoms of an element are identical| |
+|JJ Thomson|- Atoms contain negatively charged electrons, since atoms are neutral, the **rest of the atom is a positevly charged sphere**.
|
+|JJ Thomson|- Atoms contain negatively charged electrons, since atoms are neutral, the **rest of the atom is a positevly charged sphere**.
- Negatively charged electrons were **evenly distrubuted** throughout the atom.
- **Ray cathode experiment** - basically atoms were attracted to a postive end of the tube, so there most be negative charges in the atoms.
 |
| |
+|Ernest Rutherford|- Discovered that the postively charged **nucleus**.
|
+|Ernest Rutherford|- Discovered that the postively charged **nucleus**.
- The nucleus was **surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons**
- Most of the atom was just space.
- **Gold foil experiement**, alpha particles (postively charged) shot at atom, some bounced off at weird angles, so there most be a postively charged thing there.
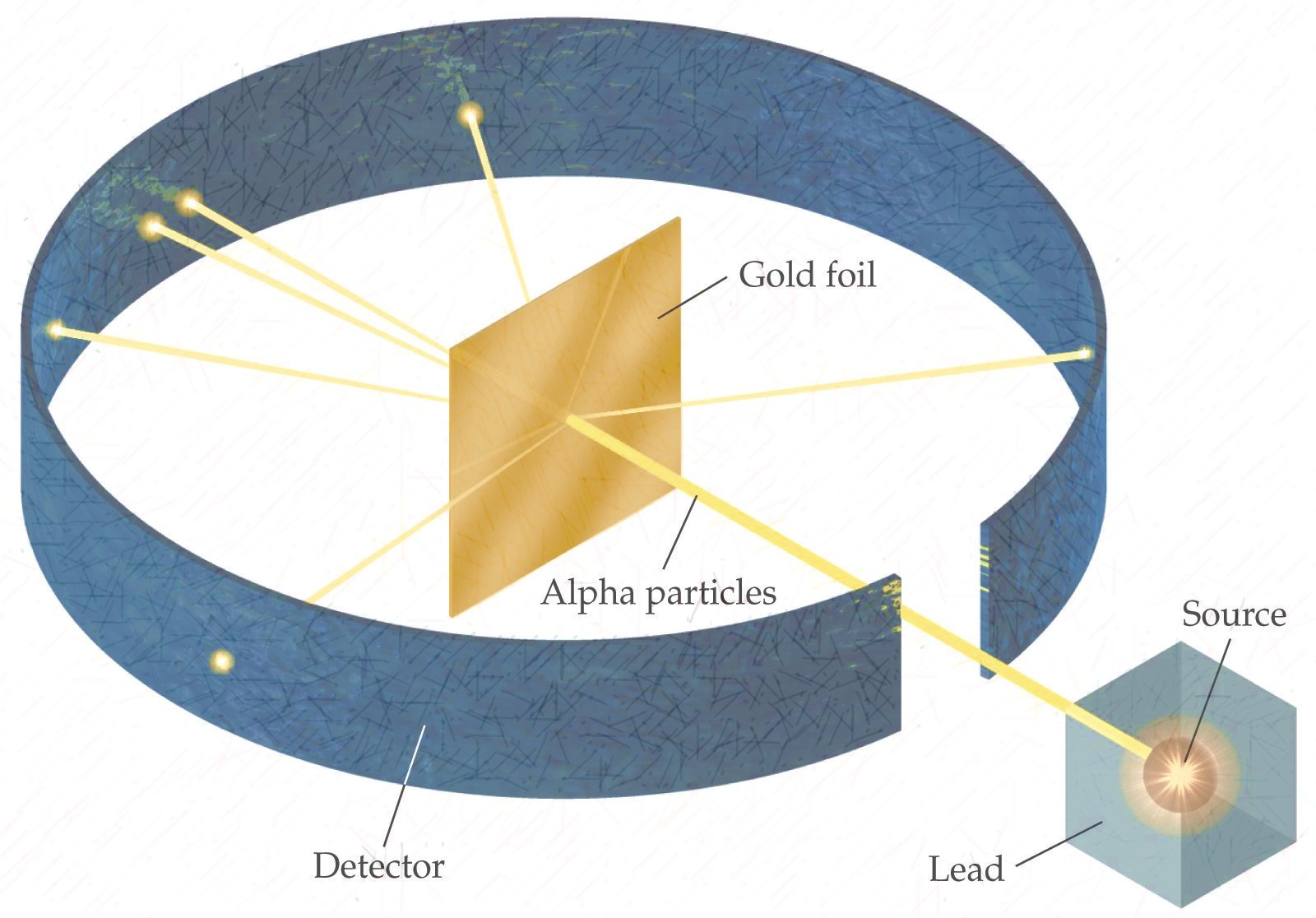 |
|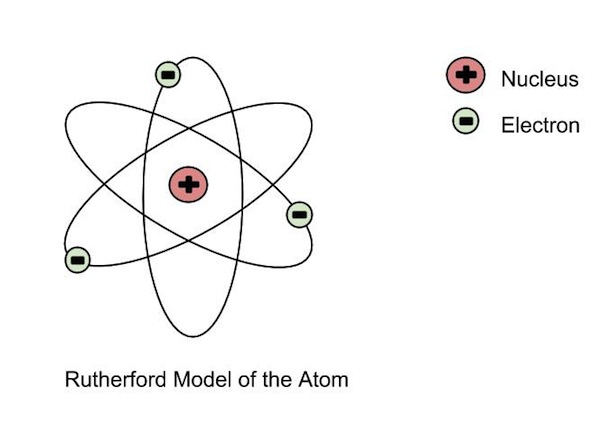 |
+|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucles = more energy.
|
+|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucles = more energy.
- Electrons **cannot** jump orbit to orbit or release energy as light going down.
- Each orbit can hold a specifc amount of electrons, `2,8,8,2`, useful for the first 20 elements| |
+|James Chadwick|- Discovered the neutron, mass of neutron = mass of proton (basically)
|
+|James Chadwick|- Discovered the neutron, mass of neutron = mass of proton (basically)
- Neutral atoms have **equal numbers** of protons and electrons.| |
+
## Carbon
@@ -258,7 +297,7 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- `Sustainable Ecosystem`
- An ecosystem that is maintained through natural processes
-- **Ecological niche**:
+- `Ecological niche`:
- Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. This is its role in an ecosystem (e.g. what it eats, what eats it, how it behaves, etc.)
- `Biodiversity`: The variety of life in a particular ecosystem, also known as biological diversity.
- Canada is home to about 140 000 to 200 000 species of plants and animals. Only 71 000 have been identified.
@@ -336,23 +375,21 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- #### REVERSE of Photosynthesis
- Sugar breaks down into **CARBON DIOXIDE** and **WATER**
- Release of energy when this happens
+
## Feeding Relationship
- Energy flow through an ecosystem in one direction, from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs (producers) and then to various hetrotrophs (consumers).
- Food are a series of steps in which organisms transfers energy by eating or eaten (pg. 43).
- Food webs show the complex interactions within an ecosystem (pg. 44).
-
- Each step in a food chain or web is called a `trophic` level. Producers make up the first step, consumers make up the higher levels. E.g. first trophic level are producers, second trophic level are primary consumers, etc.
## ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
- Food chains and food webs do not give any information about the numbers of organisms involved.
-
- This information can be shown through ecological pyramids.
-
- An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or food chain.
-
--
|
+
## Carbon
@@ -258,7 +297,7 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- `Sustainable Ecosystem`
- An ecosystem that is maintained through natural processes
-- **Ecological niche**:
+- `Ecological niche`:
- Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. This is its role in an ecosystem (e.g. what it eats, what eats it, how it behaves, etc.)
- `Biodiversity`: The variety of life in a particular ecosystem, also known as biological diversity.
- Canada is home to about 140 000 to 200 000 species of plants and animals. Only 71 000 have been identified.
@@ -336,23 +375,21 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- #### REVERSE of Photosynthesis
- Sugar breaks down into **CARBON DIOXIDE** and **WATER**
- Release of energy when this happens
+
## Feeding Relationship
- Energy flow through an ecosystem in one direction, from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs (producers) and then to various hetrotrophs (consumers).
- Food are a series of steps in which organisms transfers energy by eating or eaten (pg. 43).
- Food webs show the complex interactions within an ecosystem (pg. 44).
-
- Each step in a food chain or web is called a `trophic` level. Producers make up the first step, consumers make up the higher levels. E.g. first trophic level are producers, second trophic level are primary consumers, etc.
## ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
- Food chains and food webs do not give any information about the numbers of organisms involved.
-
- This information can be shown through ecological pyramids.
-
- An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or food chain.
-
--  +
+
+
+ |Pyramid|Description|Picture|
@@ -423,7 +460,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
--
|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
@@ -423,7 +460,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
-- 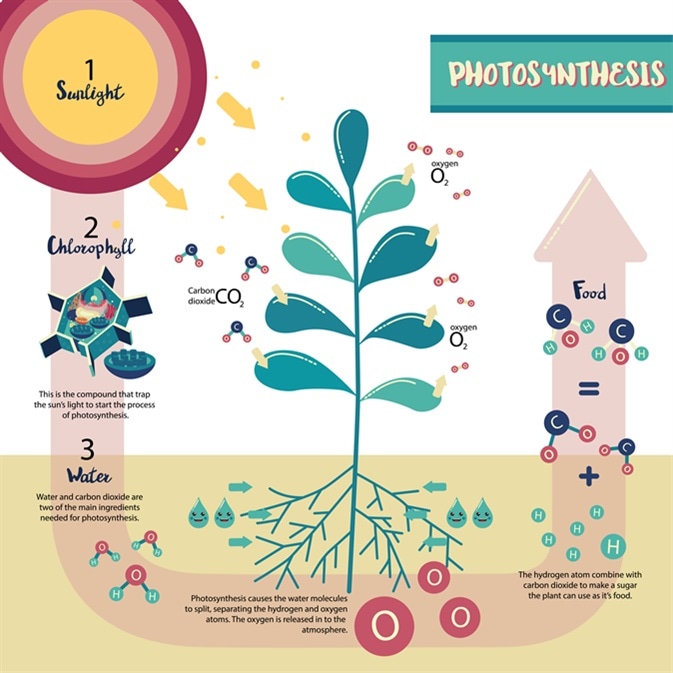 +
+
+
+ ### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
@@ -442,7 +480,7 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
### STEPS/PROCESSES
--
### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
@@ -442,7 +480,7 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
### STEPS/PROCESSES
-- 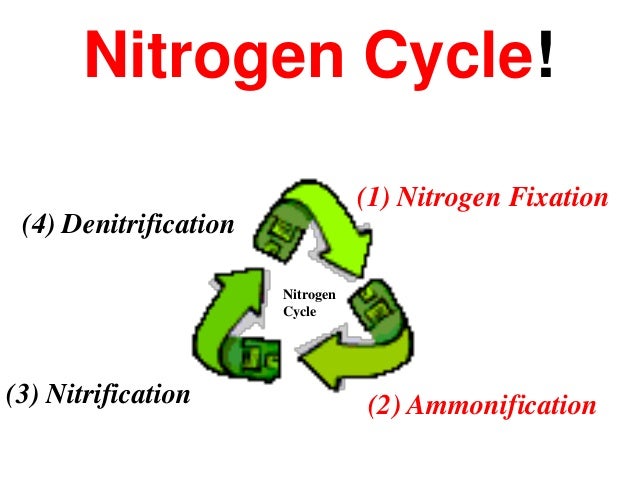 +
+ ### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -482,14 +520,6 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
-## Benefits of Succession
-- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
-- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused distrubances.
-- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rica).
-- Time needed is very long.
-- Original cause o disturbance must be eliminated.
-- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
-- Disturbances can be repaired through humans actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
@@ -536,28 +566,28 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -482,14 +520,6 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
-## Benefits of Succession
-- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
-- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused distrubances.
-- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rica).
-- Time needed is very long.
-- Original cause o disturbance must be eliminated.
-- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
-- Disturbances can be repaired through humans actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
@@ -536,28 +566,28 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- | + |
- Parasitism and Predation |
- Commensalism |
- Mutalism |
+ + |
+ Parasitism and Predation |
+ Commensalism |
+ Mutalism |
- | 0 |
+ 0 |
|
- Neutralism |
- Commensalism |
+ Neutralism |
+ Commensalism |
- | - |
- Competition |
+ - |
+ Competition |
|
- Parasitism and Predation |
+ Parasitism and Predation |
|
- - |
- 0 |
- + |
+ - |
+ 0 |
+ + |
@@ -580,7 +610,7 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- Mates.
## Candian Biomes
--  +
+ ## Ecosystem Services
- **Cultural Services**
## Ecosystem Services
- **Cultural Services**
 ## Quantitative physical Properties
- **```Density```**: amount of ```stuff``` (or mass) per unit volume (g/cm3)
@@ -147,27 +155,58 @@
- A characteristic (property) of a substance that describes its ability to undergo ```changes to its composition to produce one of more new substances. AKA BEHAVIOUR. Everything has one!```
- ```Cannot be determined by physical properties```
-
- E.g. ability of nails /cars to rust
- Fireworks are explosive
-
- Denim is resistant to soap, but is combustible
-
- Baking soda reacts with vinegar and cake ingredients to rise
-
- Bacterial cultures convert milk to cheese, grapes to wine, cocoa to chocolate
-
- CLR used to clean kettles, showerheads because it breaks down minerals
-
- Silver cleaner for tarnished jewellery, dishes because silver reacts with air to turn black.
-## Physical Change
-
-## Chemical Change
-
## Periodic Table
+
## Quantitative physical Properties
- **```Density```**: amount of ```stuff``` (or mass) per unit volume (g/cm3)
@@ -147,27 +155,58 @@
- A characteristic (property) of a substance that describes its ability to undergo ```changes to its composition to produce one of more new substances. AKA BEHAVIOUR. Everything has one!```
- ```Cannot be determined by physical properties```
-
- E.g. ability of nails /cars to rust
- Fireworks are explosive
-
- Denim is resistant to soap, but is combustible
-
- Baking soda reacts with vinegar and cake ingredients to rise
-
- Bacterial cultures convert milk to cheese, grapes to wine, cocoa to chocolate
-
- CLR used to clean kettles, showerheads because it breaks down minerals
-
- Silver cleaner for tarnished jewellery, dishes because silver reacts with air to turn black.
-## Physical Change
-
-## Chemical Change
-
## Periodic Table
+ +
+### Trends On The Periodic Table
+- The first column are the `Alkali metals`.
+ - They are shiny, have the consitency of clay, and are easily cut with a knife.
+ - They are the **most reactive** metals.
+ - They react violently with water.
+ - Alkali metals are **never found as free elements in nature**. They are always bonded with another element.
+- The second column are the `Alkaline earth metals`.
+ - They are **never found uncombined in nature**.
+- The last column are the `Noble gases`.
+ - **Extremely un-reactive**.
+- The second last column are the `Halogens`.
+ - The **most reactive non-metals**
+ - They **react with alkali metals to form salts**.
+- The middle parts are the `transition metals`.
+ - They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
+ - Usually bright coloured.
+ - They have properties similar to elements in their same family
+ - Many of them combine with oxygen to form compounds called oxides.
+- The rows outside the table are the `Inner tranistion metals`.
+
+
+
+### Trends On The Periodic Table
+- The first column are the `Alkali metals`.
+ - They are shiny, have the consitency of clay, and are easily cut with a knife.
+ - They are the **most reactive** metals.
+ - They react violently with water.
+ - Alkali metals are **never found as free elements in nature**. They are always bonded with another element.
+- The second column are the `Alkaline earth metals`.
+ - They are **never found uncombined in nature**.
+- The last column are the `Noble gases`.
+ - **Extremely un-reactive**.
+- The second last column are the `Halogens`.
+ - The **most reactive non-metals**
+ - They **react with alkali metals to form salts**.
+- The middle parts are the `transition metals`.
+ - They are good conductors of heat and electricity.
+ - Usually bright coloured.
+ - They have properties similar to elements in their same family
+ - Many of them combine with oxygen to form compounds called oxides.
+- The rows outside the table are the `Inner tranistion metals`.
+
+ +
+- The **left** to the **staircase** are the metals and the **right** are the non-metals. The ones touching the **staircase** are the `metalloids`.
+
+
+
+- The **left** to the **staircase** are the metals and the **right** are the non-metals. The ones touching the **staircase** are the `metalloids`.
+
+ +
+### How To Read An Element
+
+
+### How To Read An Element
+ +
## History of The Atom
+|Person|Description|Picture|
+|:-----|:----------|:------|
+|Democritus|All matter can be divided up into smaller pieces until it reaches an unbreakable particle called an ATOM (cannot be cut)
+
## History of The Atom
+|Person|Description|Picture|
+|:-----|:----------|:------|
+|Democritus|All matter can be divided up into smaller pieces until it reaches an unbreakable particle called an ATOM (cannot be cut) |
+|John Dalton|- Billbard model, atoms of **different elements are different**
|
+|John Dalton|- Billbard model, atoms of **different elements are different** |
| |
+|Ernest Rutherford|- Discovered that the postively charged **nucleus**.
|
+|Ernest Rutherford|- Discovered that the postively charged **nucleus**.  |
| |
+|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucles = more energy.
|
+|Niels Bohr|- Discovered that electrons **orbit the nucleus in fixed paths**, each electron has a **definite** amount of energy, further from nucles = more energy. |
+|James Chadwick|- Discovered the neutron, mass of neutron = mass of proton (basically)
|
+|James Chadwick|- Discovered the neutron, mass of neutron = mass of proton (basically) |
+
## Carbon
@@ -258,7 +297,7 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- `Sustainable Ecosystem`
- An ecosystem that is maintained through natural processes
-- **Ecological niche**:
+- `Ecological niche`:
- Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. This is its role in an ecosystem (e.g. what it eats, what eats it, how it behaves, etc.)
- `Biodiversity`: The variety of life in a particular ecosystem, also known as biological diversity.
- Canada is home to about 140 000 to 200 000 species of plants and animals. Only 71 000 have been identified.
@@ -336,23 +375,21 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- #### REVERSE of Photosynthesis
- Sugar breaks down into **CARBON DIOXIDE** and **WATER**
- Release of energy when this happens
+
## Feeding Relationship
- Energy flow through an ecosystem in one direction, from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs (producers) and then to various hetrotrophs (consumers).
- Food are a series of steps in which organisms transfers energy by eating or eaten (pg. 43).
- Food webs show the complex interactions within an ecosystem (pg. 44).
-
- Each step in a food chain or web is called a `trophic` level. Producers make up the first step, consumers make up the higher levels. E.g. first trophic level are producers, second trophic level are primary consumers, etc.
## ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
- Food chains and food webs do not give any information about the numbers of organisms involved.
-
- This information can be shown through ecological pyramids.
-
- An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or food chain.
-
--
|
+
## Carbon
@@ -258,7 +297,7 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- `Sustainable Ecosystem`
- An ecosystem that is maintained through natural processes
-- **Ecological niche**:
+- `Ecological niche`:
- Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. This is its role in an ecosystem (e.g. what it eats, what eats it, how it behaves, etc.)
- `Biodiversity`: The variety of life in a particular ecosystem, also known as biological diversity.
- Canada is home to about 140 000 to 200 000 species of plants and animals. Only 71 000 have been identified.
@@ -336,23 +375,21 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- #### REVERSE of Photosynthesis
- Sugar breaks down into **CARBON DIOXIDE** and **WATER**
- Release of energy when this happens
+
## Feeding Relationship
- Energy flow through an ecosystem in one direction, from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs (producers) and then to various hetrotrophs (consumers).
- Food are a series of steps in which organisms transfers energy by eating or eaten (pg. 43).
- Food webs show the complex interactions within an ecosystem (pg. 44).
-
- Each step in a food chain or web is called a `trophic` level. Producers make up the first step, consumers make up the higher levels. E.g. first trophic level are producers, second trophic level are primary consumers, etc.
## ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
- Food chains and food webs do not give any information about the numbers of organisms involved.
-
- This information can be shown through ecological pyramids.
-
- An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or food chain.
-
--  +
+
+
+ |Pyramid|Description|Picture|
@@ -423,7 +460,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
--
|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
@@ -423,7 +460,8 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
--  +
+
+
+ ### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
@@ -442,7 +480,7 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
### STEPS/PROCESSES
--
### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
@@ -442,7 +480,7 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
### STEPS/PROCESSES
--  +
+ ### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -482,14 +520,6 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
-## Benefits of Succession
-- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
-- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused distrubances.
-- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rica).
-- Time needed is very long.
-- Original cause o disturbance must be eliminated.
-- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
-- Disturbances can be repaired through humans actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
@@ -536,28 +566,28 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
@@ -482,14 +520,6 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
-## Benefits of Succession
-- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
-- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused distrubances.
-- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rica).
-- Time needed is very long.
-- Original cause o disturbance must be eliminated.
-- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
-- Disturbances can be repaired through humans actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
@@ -536,28 +566,28 @@ atmosphere, river to lake)
 +
+ ## Ecosystem Services
- **Cultural Services**
## Ecosystem Services
- **Cultural Services**