diff --git a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
index 7fc9a14..9082d18 100644
--- a/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
+++ b/Grade 9/Science/SNC1DZ/Study_Sheet.md
@@ -245,6 +245,8 @@ weakening, or loss of value.**
- `Sustainable Ecosystem`
- An ecosystem that is maintained through natural processes
+- **Ecological niche**:
+ - Every species interacts with other species and with its environment in a unique way. This is its role in an ecosystem (e.g. what it eats, what eats it, how it behaves, etc.)
## Types of Energy
- #### Radiant Energy
@@ -364,6 +366,91 @@ from consuming other organisms
- ALL humans are consumers (unless you’re the hulk)
+## Feeding Relationship
+- Energy flow through an ecosystem in one direction, from the sun or inorganic compounds to autotrophs (producers) and then to various hetrotrophs (consumers).
+- Food are a series of steps in which organisms transfers energy by eating or eaten (pg. 43).
+- Food webs show the complex interactions within an ecosystem (pg. 44).
+
+- Each step in a food chain or web is called a `trophic` level. Producers make up the first step, consumers make up the higher levels. E.g. first trophic level are producers, second trophic level are primary consumers, etc.
+
+## ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS
+
+- Food chains and food webs do not give any information about the numbers of organisms involved.
+
+- This information can be shown through ecological pyramids.
+
+- An ecological pyramid is a diagram that shows the amount of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a food web or food chain.
+
+-  +
+
+|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
+|:------|:----------|:------|
+|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.
+
+
+|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
+|:------|:----------|:------|
+|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.
Biomass is preferred to the use of numbers of organisms because individual organisms can vary in size. It is the `total mass` **(not the size)** that is important. Sometimes it’s inverted.
Pyramid of biomass records the total dry organic matter of organisms at each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem.| +|Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.
+|Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.
Because each trophic level harvests only about `one tenth` of the energy from the level below, it can support only about one `10th` the amount of living tissue.
**`Can be inverted`**: 1 large tree supports thousands of organisms living on it
Pyramid of numbers displays the number of individuals| |
+|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period.
|
+|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period.
**CANNOT** be inverted, due to energy transfers
**Only 10% of the energy available within one trophic level is transferred to organisms at the next trophic level**| |
+
+**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
+efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
+
+## Cycles
+
+|Cycle|Description|Picture|
+|:----|:----------|:------|
+|Water Cycle|Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth|
|
+
+**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
+efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
+
+## Cycles
+
+|Cycle|Description|Picture|
+|:----|:----------|:------|
+|Water Cycle|Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth| |
+|Carbon Cycle|Main Pathway – in and out of living matter|
|
+|Carbon Cycle|Main Pathway – in and out of living matter| |
+|Nitrogen Cycle|
+
+## Water Cycle
+
+### Key Terms:
+- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to
+atmosphere, river to lake)
+ - Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Percolation (Infiltration), Run-off
+ - Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
+
+### STEPS/PROCESS:
+
+- Exchange of energy leads to:
+ - Temperature Change, Climate
+ - Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp
+ - Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp
+
+- **Evaporation**:
+ - purifies the water
+ - New fresh water for the land
+
+- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
+ - Transports minerals across the globe
+
+- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
+ - Erosion and sedimentation
+
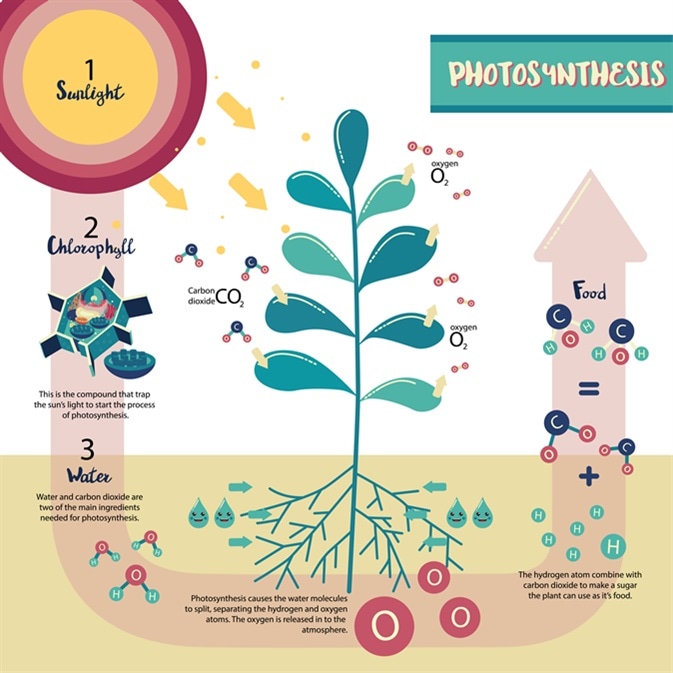
+## Carbon Cycle
+- Fourth most abundant element in universe
+- Building block of all living things
+
+
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+- All living organisms contain carbon
+- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
+- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
+- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
+-
|
+|Nitrogen Cycle|
+
+## Water Cycle
+
+### Key Terms:
+- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to
+atmosphere, river to lake)
+ - Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Percolation (Infiltration), Run-off
+ - Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
+
+### STEPS/PROCESS:
+
+- Exchange of energy leads to:
+ - Temperature Change, Climate
+ - Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp
+ - Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp
+
+- **Evaporation**:
+ - purifies the water
+ - New fresh water for the land
+
+- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
+ - Transports minerals across the globe
+
+- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
+ - Erosion and sedimentation
+
+## Carbon Cycle
+- Fourth most abundant element in universe
+- Building block of all living things
+
+
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+- All living organisms contain carbon
+- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
+- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
+- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
+-  +
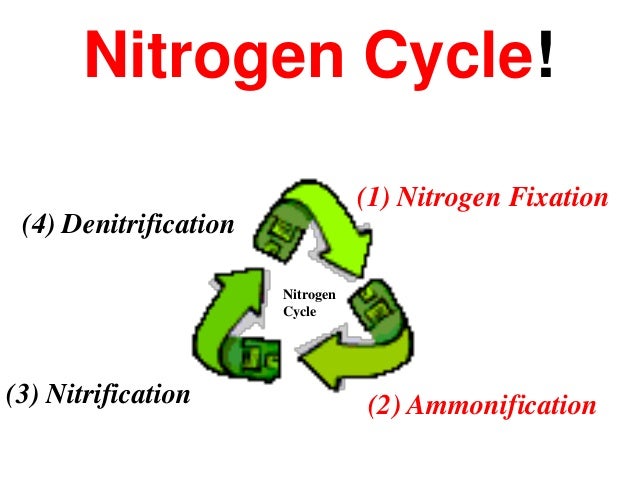
+## Nitrogen Cycle
+- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
+- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
+- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: Whenit is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
+- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
+- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
+ - Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
+ - Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+-
+
+## Nitrogen Cycle
+- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
+- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
+- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: Whenit is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
+- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
+- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
+ - Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
+ - Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+-  +
+### Nitrogen Fixation
+
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
+
+### Nitrogen Fixation
+
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
 +
+
+|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
+|:------|:----------|:------|
+|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.
+
+
+|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
+|:------|:----------|:------|
+|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.  +|Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.
+|Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.  |
+|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period.
|
+|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period. |
+
+**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
+efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
+
+## Cycles
+
+|Cycle|Description|Picture|
+|:----|:----------|:------|
+|Water Cycle|Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth|
|
+
+**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
+efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
+
+## Cycles
+
+|Cycle|Description|Picture|
+|:----|:----------|:------|
+|Water Cycle|Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth| |
+|Carbon Cycle|Main Pathway – in and out of living matter|
|
+|Carbon Cycle|Main Pathway – in and out of living matter| |
+|Nitrogen Cycle|
+
+## Water Cycle
+
+### Key Terms:
+- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to
+atmosphere, river to lake)
+ - Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Percolation (Infiltration), Run-off
+ - Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
+
+### STEPS/PROCESS:
+
+- Exchange of energy leads to:
+ - Temperature Change, Climate
+ - Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp
+ - Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp
+
+- **Evaporation**:
+ - purifies the water
+ - New fresh water for the land
+
+- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
+ - Transports minerals across the globe
+
+- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
+ - Erosion and sedimentation
+
+## Carbon Cycle
+- Fourth most abundant element in universe
+- Building block of all living things
+
+
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+- All living organisms contain carbon
+- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
+- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
+- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
+-
|
+|Nitrogen Cycle|
+
+## Water Cycle
+
+### Key Terms:
+- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to
+atmosphere, river to lake)
+ - Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Percolation (Infiltration), Run-off
+ - Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
+
+### STEPS/PROCESS:
+
+- Exchange of energy leads to:
+ - Temperature Change, Climate
+ - Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp
+ - Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp
+
+- **Evaporation**:
+ - purifies the water
+ - New fresh water for the land
+
+- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
+ - Transports minerals across the globe
+
+- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
+ - Erosion and sedimentation
+
+## Carbon Cycle
+- Fourth most abundant element in universe
+- Building block of all living things
+
+
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+- All living organisms contain carbon
+- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
+- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
+- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
+-  +
+## Nitrogen Cycle
+- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
+- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
+- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: Whenit is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
+- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
+- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
+ - Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
+ - Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+-
+
+## Nitrogen Cycle
+- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
+- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
+- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: Whenit is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
+- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
+- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
+ - Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
+ - Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
+### STEPS/PROCESSES
+-  +
+### Nitrogen Fixation
+
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
+
+### Nitrogen Fixation
+
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.