 |Pyramid|Description|Picture|
|:------|:----------|:------|
|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.
|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
|:------|:----------|:------|
|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.  |Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.
|Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.  |
|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period.
|
|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period. |
**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
## Biogeochemical Cycles
|Cycle|Picture|
|:----|:------|
|Water Cycle|
|
**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
## Biogeochemical Cycles
|Cycle|Picture|
|:----|:------|
|Water Cycle| |
|Carbon Cycle|
|
|Carbon Cycle| |
|Nitrogen Cycle|
|
|Nitrogen Cycle| |
## Water Cycle
- Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth.
- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to atmosphere, river to lake)
- Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
### Steps/Process:
- Exchange of energy leads to:
- Temperature Change, Climate.
- Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp, water cooles and collects in clouds.
- Precipitation 🡪 After condensation, water falls down from the clouds in the form of prefcipitation, can be commonly described as rain.
- Transpiration 🡪 Water leaves from plants, plants losing water to air.
- Infiltration/percolation 🡪 Water seeps into the ground, in between small cracks in the rocks and the Earth.
- Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp.
- Surface Run Off 🡪 Water flows above the ground.
### Importance
- **Evaporation**:
- Purifies the water.
- New fresh water for the land
- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
- Transports minerals across the globe.
- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
- Erosion and sedimentation.
### Human Inpacts
- Humans building dams (flooding is a problem!).
- Deforestation contributes to global warming, hence melting glaciers and causing flooding in cities.
- (Also less transpiration from clear cutting) – pg. 48.
- Factories and cars pollute the air, leading to acid precipitation.
- Oil spills destroy aquatic ecosystems.
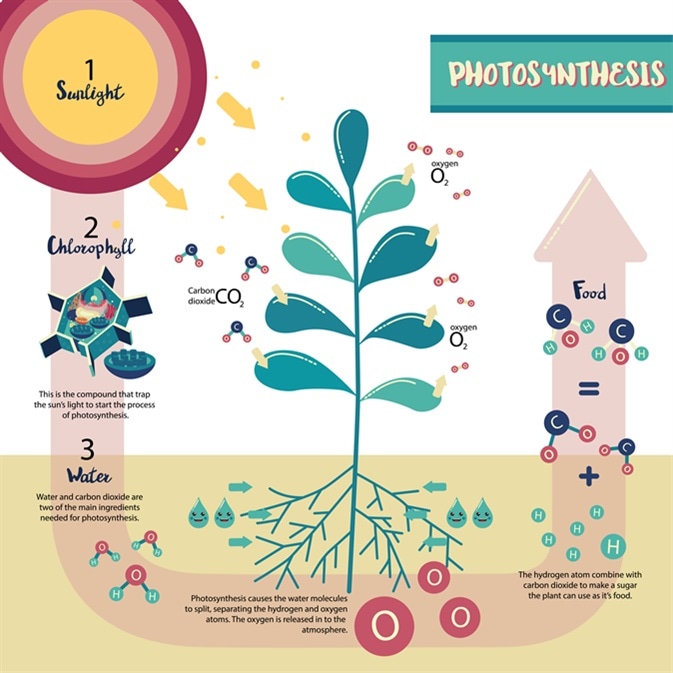
## Carbon Cycle
- Fourth most abundant element in universe
- Building block of all living things
- Main Pathway – in and out of living matter
- All living organisms contain carbon.
### Steps/Process
- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
- Light Energy 🡪 Chemical Energy
- Photosynthesis 🡪 converts carbon into sugr to form simple sugars.
- Biodegration 🡪 Animal remains decompose and turn into fossil fuels.
- Respiration 🡪 Animals respirate and give off carbon into the atmophere.
- Burning of fossil fuels 🡪 Release the carbon contained in the fossil fuels.
### Importance
- **Phtosynthesis**
- CO2 is converted to glucose using water and sunlight
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
|
## Water Cycle
- Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth.
- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to atmosphere, river to lake)
- Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
### Steps/Process:
- Exchange of energy leads to:
- Temperature Change, Climate.
- Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp, water cooles and collects in clouds.
- Precipitation 🡪 After condensation, water falls down from the clouds in the form of prefcipitation, can be commonly described as rain.
- Transpiration 🡪 Water leaves from plants, plants losing water to air.
- Infiltration/percolation 🡪 Water seeps into the ground, in between small cracks in the rocks and the Earth.
- Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp.
- Surface Run Off 🡪 Water flows above the ground.
### Importance
- **Evaporation**:
- Purifies the water.
- New fresh water for the land
- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
- Transports minerals across the globe.
- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
- Erosion and sedimentation.
### Human Inpacts
- Humans building dams (flooding is a problem!).
- Deforestation contributes to global warming, hence melting glaciers and causing flooding in cities.
- (Also less transpiration from clear cutting) – pg. 48.
- Factories and cars pollute the air, leading to acid precipitation.
- Oil spills destroy aquatic ecosystems.
## Carbon Cycle
- Fourth most abundant element in universe
- Building block of all living things
- Main Pathway – in and out of living matter
- All living organisms contain carbon.
### Steps/Process
- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
- Light Energy 🡪 Chemical Energy
- Photosynthesis 🡪 converts carbon into sugr to form simple sugars.
- Biodegration 🡪 Animal remains decompose and turn into fossil fuels.
- Respiration 🡪 Animals respirate and give off carbon into the atmophere.
- Burning of fossil fuels 🡪 Release the carbon contained in the fossil fuels.
### Importance
- **Phtosynthesis**
- CO2 is converted to glucose using water and sunlight
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
 ### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: When it is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
### Steps/Process
- Nitrogen gets fixed, but still needs to be broken in to **usable form**. It travels through the ground. `Ammonium` gets produced from the fixed nitrogen, then `nitrifying` bacteria turns that into **`nitrites`**, which is **NOT** usable yet. Nitrifying bacteria then convert **nirites** into **usable nitorgen**, **`nitrates`**.
- Plants then use **`nitrates`** for energy, where then **decomposers** turn into ammonium.
- Denitrification 🡪 `Denitrifying` bacteria break down **`nitrates`**, **usable nitrogen** back into atmospheric nitrogen.
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
- These microorganisms convert nitrogen gas into a variety of nitrogen containing compounds such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia
- Lightning and UV radiation also fix small amounts of it
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
- Lightning Storms
- stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
1. Free living Bacteria
- Highly specialized bacteria live in the soil and have the ability to combine atmospheric nitrogen with hydrogen to make ammonium(NH4+).
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
- This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
### Human Impacts
- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
- These can be classified into two categories.
1. `Density dependent factors`
2. `Density independent factors`
### Density Independent Factors
- DIF’s can affect a population no matter what its density is. The effect of the factor (such as weather) on the size of the population **does not** depend on the **original size** of the population.
- Examples:
- unusual weather
- natural disasters
- seasonal cycles
- certain human activities—such as damming rivers and clear-cutting forests
### Density Dependent Factors
- DDF’s affect a population **ONLY** when it reaches a certain size. The effect of the factor (such as disease) on the size of the population depends on the **original size** of the population
- Examples:
- Competition
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Disease
## Relationships
1. **Symbiosis**
- Two different organisms associate with each other in a close way.
- Is the interaction between members of `two different species` that live together in a close association.
- **Mutualism (+/+)**
- Both species benefit from the relationship.
- (eg. human intestine and good bacteria, bees and flowers, clownfish and sea anemone, cattle egret and cow).
- **Commensalism (+/0)**
- one species benefits, the other is **unaffected**.
- (eg. beaver cutting down trees, whales and barancles).
- **Parasitism (-/+)**
- one species is harmed, the other **benefits**.
- (eg. lice and humans, mosquito and humans).
- **Competition (-/-)**
- neither species benefits. Can be harmed. (-/-).
- **Neutralism (0/0)**
- both species are unaffected (unlikely).
- True neutralism is extremely unlikely or even impossible to prove. One cannot assert positively that there is absolutely no competition between or benefit to either species.
- Example: fish and dandelion
### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: When it is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
### Steps/Process
- Nitrogen gets fixed, but still needs to be broken in to **usable form**. It travels through the ground. `Ammonium` gets produced from the fixed nitrogen, then `nitrifying` bacteria turns that into **`nitrites`**, which is **NOT** usable yet. Nitrifying bacteria then convert **nirites** into **usable nitorgen**, **`nitrates`**.
- Plants then use **`nitrates`** for energy, where then **decomposers** turn into ammonium.
- Denitrification 🡪 `Denitrifying` bacteria break down **`nitrates`**, **usable nitrogen** back into atmospheric nitrogen.
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
- These microorganisms convert nitrogen gas into a variety of nitrogen containing compounds such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia
- Lightning and UV radiation also fix small amounts of it
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
- Lightning Storms
- stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
1. Free living Bacteria
- Highly specialized bacteria live in the soil and have the ability to combine atmospheric nitrogen with hydrogen to make ammonium(NH4+).
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
- This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
### Human Impacts
- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
- These can be classified into two categories.
1. `Density dependent factors`
2. `Density independent factors`
### Density Independent Factors
- DIF’s can affect a population no matter what its density is. The effect of the factor (such as weather) on the size of the population **does not** depend on the **original size** of the population.
- Examples:
- unusual weather
- natural disasters
- seasonal cycles
- certain human activities—such as damming rivers and clear-cutting forests
### Density Dependent Factors
- DDF’s affect a population **ONLY** when it reaches a certain size. The effect of the factor (such as disease) on the size of the population depends on the **original size** of the population
- Examples:
- Competition
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Disease
## Relationships
1. **Symbiosis**
- Two different organisms associate with each other in a close way.
- Is the interaction between members of `two different species` that live together in a close association.
- **Mutualism (+/+)**
- Both species benefit from the relationship.
- (eg. human intestine and good bacteria, bees and flowers, clownfish and sea anemone, cattle egret and cow).
- **Commensalism (+/0)**
- one species benefits, the other is **unaffected**.
- (eg. beaver cutting down trees, whales and barancles).
- **Parasitism (-/+)**
- one species is harmed, the other **benefits**.
- (eg. lice and humans, mosquito and humans).
- **Competition (-/-)**
- neither species benefits. Can be harmed. (-/-).
- **Neutralism (0/0)**
- both species are unaffected (unlikely).
- True neutralism is extremely unlikely or even impossible to prove. One cannot assert positively that there is absolutely no competition between or benefit to either species.
- Example: fish and dandelion
| + | Parasitism and Predation | Commensalism | Mutalism |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Neutralism | Commensalism | |
| - | Competition | Parasitism and Predation | |
| - | 0 | + |
 ### Tundra
* Most **NORTHERN** biome of Canada.
* Low temperatures + lots of **PERMAFROST**
* Low decomposition rate.
* Plants grow slower due to cold
* `Species`: Polar bears, Caribou, Arctic foxes.
### Boreal Forest
* **Largest** biome in Canada.
* Warmer weather+plenty rainfall.
* Acidic Soil - Limits variety of plants + slows down decomposition.
* `Species` Grey wolves, conifers, moss, black bears.
### Grassland
* Moderate rainfall (supports grass not trees).
* Dry $`\rightarrow`$ Fire $`\rightarrow`$ Fire prevents larges trees from growing.
* Very **Fertile** black soil (high decomposition rate)
* Large portions of this biome are replaced by farms in Canada.
* `Species`: Bison, Snakes, fescue grasses, voles.
### Temperate Deciduous Forest
* Layers of canopy trees, understorey trees, shrubs, ground vegetation.
* Variety oof plants + species.
* Fast decomposition rate (warm temperatures).
* Large portions of this biome used by humans for cities.
* `Species`: Shrews, decidious trees, deer, black bears.
### Mountain Forest
* Temperatures vary with elevation
* Windy + cool summers
* Heavy precipitation on leeward side of mountains
* `Species` Elk, cougar, large coniferous trees, ferns.
## Biodiversity
- There are alot of threats to biodiversity, pollution, invasive species etc.
### Pollution / Habitat Loss
- Pollution is caused everywhere and disrupts ecosystems. Like plastic pollution, which has killed many marine life such as turtle, as they believe plastic bags are jellfish and eats it and dies.
- We can easily manage this, by just reducing the amount of pllution done.
- Habitat loss is a result due to our greedy mind for resources such as trees. We deforest lots of trees, using unsustainable methods, such as **clear-cuttig**.
- We can easily manage this, with things such as **stewardship**, and using sustainble methods such as **selective cutting**.
### Invasive Species
- Introduction usually fails because few species can tolerate an entirely new environment.
- Can adapt to abiotic environment, may have difficulty finding food/cant deal with competition.
#### Impacts
- **Ecological**
- Competition, food, alter nutrient cycles.
- **Economic**
- Damage forests/crops = financial loss, diseases/pests destroy crops, trees and livestock.
- **Tourism**
- Species loss and reduced water quality = poor wildlife viewing, fishing and water based activities.
- Waterways choked with invasive aquatic plants = no boats.
- **Health**
- Cause disease (west nile), pesticides used for control cause pollution and are health risks.
#### Controlling Measures
1. **Chemical Control**
- Most widely used = pesticides.
- Used on forest/agricultural pests.
- Pesticides dramatically reduce crop damage.
- Environmental Risks.
- May kill non-target native species/pollute air, water, soil.
2. **Mechanical Control**
- Physical barriers or removal (cut down, burned, hunted).
- Ex. Hamilton Harbour barrier to prevent Carp invasion.
3. **Biological Control**
- Challenging but effective.
- Uses intentionally introduced organisms to control the invasive species.
- Ex. 3 insect species released in Ontario to control purple loosestrife (invasive plant that grows in wetlands).
- Tests indicated the insects are unlikely to feed on native plants.
- Rarely eradicates an invasive species … may reduce population sizes to tolerable levels.
## Introducing Ecosystems
- Most ecosystems are **SUSTAINABLE**.
- Usually, a bigger food web/food chains are more sustainable, as its more resilent to change.
### Tundra
* Most **NORTHERN** biome of Canada.
* Low temperatures + lots of **PERMAFROST**
* Low decomposition rate.
* Plants grow slower due to cold
* `Species`: Polar bears, Caribou, Arctic foxes.
### Boreal Forest
* **Largest** biome in Canada.
* Warmer weather+plenty rainfall.
* Acidic Soil - Limits variety of plants + slows down decomposition.
* `Species` Grey wolves, conifers, moss, black bears.
### Grassland
* Moderate rainfall (supports grass not trees).
* Dry $`\rightarrow`$ Fire $`\rightarrow`$ Fire prevents larges trees from growing.
* Very **Fertile** black soil (high decomposition rate)
* Large portions of this biome are replaced by farms in Canada.
* `Species`: Bison, Snakes, fescue grasses, voles.
### Temperate Deciduous Forest
* Layers of canopy trees, understorey trees, shrubs, ground vegetation.
* Variety oof plants + species.
* Fast decomposition rate (warm temperatures).
* Large portions of this biome used by humans for cities.
* `Species`: Shrews, decidious trees, deer, black bears.
### Mountain Forest
* Temperatures vary with elevation
* Windy + cool summers
* Heavy precipitation on leeward side of mountains
* `Species` Elk, cougar, large coniferous trees, ferns.
## Biodiversity
- There are alot of threats to biodiversity, pollution, invasive species etc.
### Pollution / Habitat Loss
- Pollution is caused everywhere and disrupts ecosystems. Like plastic pollution, which has killed many marine life such as turtle, as they believe plastic bags are jellfish and eats it and dies.
- We can easily manage this, by just reducing the amount of pllution done.
- Habitat loss is a result due to our greedy mind for resources such as trees. We deforest lots of trees, using unsustainable methods, such as **clear-cuttig**.
- We can easily manage this, with things such as **stewardship**, and using sustainble methods such as **selective cutting**.
### Invasive Species
- Introduction usually fails because few species can tolerate an entirely new environment.
- Can adapt to abiotic environment, may have difficulty finding food/cant deal with competition.
#### Impacts
- **Ecological**
- Competition, food, alter nutrient cycles.
- **Economic**
- Damage forests/crops = financial loss, diseases/pests destroy crops, trees and livestock.
- **Tourism**
- Species loss and reduced water quality = poor wildlife viewing, fishing and water based activities.
- Waterways choked with invasive aquatic plants = no boats.
- **Health**
- Cause disease (west nile), pesticides used for control cause pollution and are health risks.
#### Controlling Measures
1. **Chemical Control**
- Most widely used = pesticides.
- Used on forest/agricultural pests.
- Pesticides dramatically reduce crop damage.
- Environmental Risks.
- May kill non-target native species/pollute air, water, soil.
2. **Mechanical Control**
- Physical barriers or removal (cut down, burned, hunted).
- Ex. Hamilton Harbour barrier to prevent Carp invasion.
3. **Biological Control**
- Challenging but effective.
- Uses intentionally introduced organisms to control the invasive species.
- Ex. 3 insect species released in Ontario to control purple loosestrife (invasive plant that grows in wetlands).
- Tests indicated the insects are unlikely to feed on native plants.
- Rarely eradicates an invasive species … may reduce population sizes to tolerable levels.
## Introducing Ecosystems
- Most ecosystems are **SUSTAINABLE**.
- Usually, a bigger food web/food chains are more sustainable, as its more resilent to change.
| Ecosystem | Key abiotic factors | Human action and result |
|---|---|---|
| Terrestrial Ecosystems | Light availability Water availability Nutrient availability Temperature |
Clear-cutting and fire remove shade and expose the remaining organisms to much more light Damming rivers and draining swamps and marshes change water availability. Irrigation increases water availability Farming practices may increase or decrease nutrient levels in the soil. Global warming is decreasing suitable habitat for many cool-adapted species. |
| Aquatic Ecosystems | Light availability Nutrient availability Acidity Temperature Salinity |
Activities that increase erosion or stir up the bottom cloud the water and reduce light penetration. Nutrient runoff from agriculture and urban enviornments increases the nutrient content of surface water and groundwater, causing algal blooms Acidic air pollution results in acid precipitation. Carbon dioxide emissions produced by the burning of fossil fuels are increasing the acidity of the oceans. Industries and power plants release heated waste water into lakes and rivers, killing fish and other organisms. Salting highways and long-term irrigation practices can cause salt to accumlate. |