| Word | Definition (or diagram/translation) |
|---|---|
| Particle Theory of Matter | Theory that describes the composition and behaviour of matter as being composed of small particles with empty space |
| Matter | Substance that has mass and occupies space |
| Mechanical Mixture | A heterogeneous mixture which one can physically separate |
| Suspension | A heterogeneous mixture where insoluble solid particles are distributed throughout a fluid, floating freely/td> |
| Alloy | A combination of 2+ metals |
| Mixture | A substance that is made up of at least 2 types of particles |
| Qualitative property | A property of a substance that is not measured and doesn't have a numerical value, such as colour, odour, and texture |
| Qualitative observation | An numerical observation |
| Precipitate | A solid that separates from a solution |
| Density | A measure of how much mass is contained in a given unit volume of a substance; calculated by dividing the mass of a sample of its volume (mass/volume) |
| Element | Element An element is made up of the same atoms throughout, and cannot be broken down further |
| Metal | a solid material that is typically hard, shiny, malleable, fusible, and ductile, with good electrical and thermal conductivity |
| Pure substance | A substance that is made up of only one type of particle |
| Atom | The smallest unit of matter found in substances |
| Solution | A uniform mixture of 2 or more substances |
| Colloid | is substance with small particles suspended in it, unable to be separated by gravity |
| Emulsion | A mixture of 2 insoluble liquids, in which one liquid is suspended in the other |
| Physical Property | Characteristic of a substance that can be determined without changing the makeup of the substance |
| Characteristic | A physical property that is unique to a substance and can be used to identify the substance |
| Periodic Table | a table of the chemical elements arranged in order of atomic number, usually in rows, so that elements with similar atomic structure (and hence similar chemical properties) appear in vertical columns. |
| Compound | Compounds are chemically joined atoms of different elements |
| Non-Metal | A substance that isn’t a metal |
 |Pyramid|Description|Picture|
|:------|:----------|:------|
|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.
|Pyramid|Description|Picture|
|:------|:----------|:------|
|Pyramid of Biomass|Show the **total** amout of `living tissue` available at each `trophic` level. This shows the amount of tissue available for the next `trophic` level.  |Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.
|Numbers Pyramids|Shows the number of organisms at each trophic level per unit area of an ecosystem.  |
|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period.
|
|Energy Pyramid|Shows the amount of energy input to each trophic level in a given area of an ecosystem over an extended period. |
**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
## Cycles
|Cycle|Picture|
|:----|:------|
|Water Cycle|
|
**NOTE FOR ENERGY PYRAMIDS**: In nature, ecological
efficiency varies from `5%` to `20%` energy available between successive trophic levels (`95%` to `80%` loss). About 10% efficiency is a general rule. `Rule of 10’s` at each level.
## Cycles
|Cycle|Picture|
|:----|:------|
|Water Cycle| |
|Carbon Cycle|
|
|Carbon Cycle| |
|Nitrogen Cycle|
|
|Nitrogen Cycle| |
## Water Cycle
- Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth
### Key Terms:
- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to
atmosphere, river to lake)
- Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Percolation (Infiltration), Run-off
- Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
### STEPS/PROCESS:
- Exchange of energy leads to:
- Temperature Change, Climate
- Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp
- Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp
- **Evaporation**:
- purifies the water
- New fresh water for the land
- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
- Transports minerals across the globe
- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
- Erosion and sedimentation
### Human Inpacts
- Humans building dams (flooding is a problem!)
- Deforestation contributes to global warming, hence melting glaciers and causing flooding in cities
- (Also less transpiration from clear cutting) – pg. 48
- Factories and cars pollute the air, leading to acid precipitation
- Oil spills destroy aquatic ecosystems
## Carbon Cycle
- Fourth most abundant element in universe
- Building block of all living things
- Main Pathway – in and out of living matter
### STEPS/PROCESSES
- All living organisms contain carbon
- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
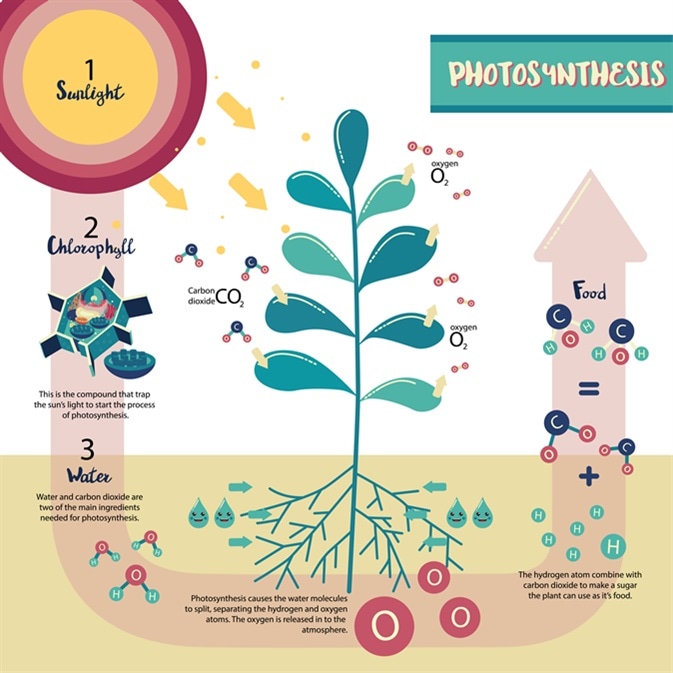
- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
- Carbon dioxide is `returned to the enviornment by:
1. `Resipiration` in plants, animals & micro-organisms.
2. `Decay` caused by micro-organisms (decompoers).
3. `Combustion` i.e. Burning fossil fuels.
- **Phtosynthesis**
- CO2 is converted to glucose using water and sunlight
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
-
|
## Water Cycle
- Continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth
### Key Terms:
- Water moves from one reservoir to another (ocean to
atmosphere, river to lake)
- Evaporation, Condensation, Precipitation, Percolation (Infiltration), Run-off
- Forms: Solid (ice), Liquid (water), Gas (vapour)
### STEPS/PROCESS:
- Exchange of energy leads to:
- Temperature Change, Climate
- Condenses 🡪 occurs during cooler temp
- Evaporation 🡪 happens during warmer temp
- **Evaporation**:
- purifies the water
- New fresh water for the land
- **Flow of liquid water and ice**
- Transports minerals across the globe
- **Reshaping the geological features of Earth**
- Erosion and sedimentation
### Human Inpacts
- Humans building dams (flooding is a problem!)
- Deforestation contributes to global warming, hence melting glaciers and causing flooding in cities
- (Also less transpiration from clear cutting) – pg. 48
- Factories and cars pollute the air, leading to acid precipitation
- Oil spills destroy aquatic ecosystems
## Carbon Cycle
- Fourth most abundant element in universe
- Building block of all living things
- Main Pathway – in and out of living matter
### STEPS/PROCESSES
- All living organisms contain carbon
- CO2 is a waste product of cellular respiration
- Plants use carbon dioxide and water to form simple sugars (photosynthesis)
- Light Energy --> Chemical Energy
- Carbon dioxide is `returned to the enviornment by:
1. `Resipiration` in plants, animals & micro-organisms.
2. `Decay` caused by micro-organisms (decompoers).
3. `Combustion` i.e. Burning fossil fuels.
- **Phtosynthesis**
- CO2 is converted to glucose using water and sunlight
- **Cellular Respiration**
- Breaks down glucose to release energy, expel CO2
- **Oceans are a HUGE carbon sink**.
-  ### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: Whenit is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
### STEPS/PROCESSES
-
### Human Impacts
- **Mining & burning fossil fuels**: Speed up release of CO2 to the atmosphere.
- **Deforestation & clearing vegetation**: ↑ CO2 in atmosphere.
- **Acid rain**: release CO2 from limestone.
- CO2 in the atmosphere is now higher than it has been in at least **800 000 years**.
## Nitrogen Cycle
- The most abudant gas in the atmopshere (~78%)
- `Nitrogen Fixation`: The process that causes the strong two-atom nitrogen molecules found in the atmopshere to break apart so they can combine with other atoms.
- `Nitrogen gets fixed`: Whenit is combined with oxygen or hydrogen.
- An essential component of DNA, RNA, and protenis - the building blocks of life.
- Atmopspheric nitrogen = N2
- Most living organisms are `unable` to use this form of nitrogen
- Therefore, must be **converted** to a usable form!
### STEPS/PROCESSES
- 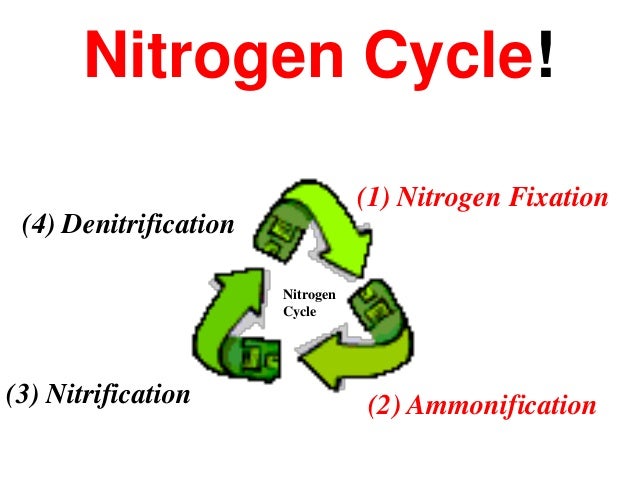 ### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
- These microorganisms convert nitrogen gas into a variety of nitrogen containing compounds such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia
- Lightning and UV radiation also fix small amounts of it
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
- Lightning Storms
- stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
1. Free living Bacteria
- Highly specialized bacteria live in the soil and have the ability to combine atmospheric nitrogen with hydrogen to make ammonium(NH4+).
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
- This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
### Human Impacts
- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Nutrient Recycling
- There is a `limited` amount of `nutrients` on earth
- e.g. you are probably aware of the water cycle – where water is
constantly being `recycled` in nature.
- There are similar cycles for all nutrients.
- When plants and animals die, their nutrient content is `not wasted`.
- Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment (i.e. into the soil, nearby water and air).
- Nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material.
- This material is passed on down the food chains and is reused by all the chain members.
- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused distrubances.
- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rica).
- Time needed is very long.
- Original cause o disturbance must be eliminated.
- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
- Disturbances can be repaired through humans actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
- These can be classified into two categories.
1. `Density dependent factors`
2. `Density independent factors`
## Density Independent Factors
- DIF’s can affect a population no matter what its density is. The effect of the factor (such as weather) on the size of the population **does not** depend on the **original size** of the population.
- Examples:
- unusual weather
- natural disasters
- seasonal cycles
- certain human activities—such as damming rivers and clear-cutting forests
## Density Dependent Factors
- DDF’s affect a population **ONLY** when it reaches a certain size. The effect of the factor (such as disease) on the size of the population depends on the **original size** of the population
- Examples:
- Competition
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Disease
## Relationships
1. **Symbiosis**
- Two different organisms associate with each other in a close way.
- Is the interaction between members of `two different species` that live together in a close association.
- Types
- **Mutualism (+/+)**
- Both species benefit from the relationship.
- (eg. human intestine and good bacteria, bees and flowers, clownfish and sea anemone, cattle egret and cow).
- **Commensalism (+/0)**
- one species benefits, the other is **unaffected**.
- (eg. beaver cutting down trees, whales and barancles).
- **Parasitism (-/+)**
- one species is harmed, the other **benefits**.
- (eg. lice and humans, mosquito and humans).
- **Competition (-/-)**
- neither species benefits. Can be harmed. (-/-).
- **Neutralism (0/0)**
- both species are unaffected (unlikely).
- True neutralism is extremely unlikely or even impossible to prove. One cannot assert positively that there is absolutely no competition between or benefit to either species.
- Example: fish and dandelion
### Nitrogen Fixation
- Most of the nitrogen used by living things is taken from the atmosphere by certain bacteria in a process called `nitrogen fixation`.
- These microorganisms convert nitrogen gas into a variety of nitrogen containing compounds such as nitrates, nitrites, and ammonia
- Lightning and UV radiation also fix small amounts of it
- Humans add nitrogen to soil through fertilizer
- 3 ways nitrogen to get fixed
1. Atmopheric Fixation
- Lightning Storms
- stroms and fuel burning in car engines produce nitrates, which are washed by rain into soil water.
2. Industrial Fixation
3. Biological Fixation
- 2 types
1. Free living Bacteria
- Highly specialized bacteria live in the soil and have the ability to combine atmospheric nitrogen with hydrogen to make ammonium(NH4+).
- Nitrogen changes into ammonium.
2. Symbiotic Relationship Bacteria
- Bacteria live in the roots of legume family plants and provide the plants with ammonium(NH4+) in exchange for the plant's carbon and a protected biome.
- `Nitrites` are absorbed by plant roots and converted to plant protein.
- `Nitrates` **can be absorbed by other plants** to continue the cycle.
- `Denitrifying bacteria` convert soil nitrates into N2 gas
- This is a `loss` of N2 from the cycle
### Human Impacts
- Nitrates also `enters` the cycle **through the addition of nitrogen rich fertilizers to the soil** – made industrially from nitrogen gas (Eutrophication – pg. 60)
- Factories release NO compounds (acid rain)
## Nutrient Recycling
- There is a `limited` amount of `nutrients` on earth
- e.g. you are probably aware of the water cycle – where water is
constantly being `recycled` in nature.
- There are similar cycles for all nutrients.
- When plants and animals die, their nutrient content is `not wasted`.
- Bacteria and fungi decompose the remains and release the nutrients back into the abiotic environment (i.e. into the soil, nearby water and air).
- Nutrients are then taken up by other plants and used to make new organic material.
- This material is passed on down the food chains and is reused by all the chain members.
- When death occurs for these members, the nutrients are again returned to the abiotic environment and the cycling of nutrients continues in this circular way.
- This ensures that there is no real longterm drain on the Earth’s nutrients, despite millions of years of plant and animal activity.
## Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosysmtems maintain their long term sustainability.
- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused distrubances.
- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rica).
- Time needed is very long.
- Original cause o disturbance must be eliminated.
- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
- Disturbances can be repaired through humans actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Changes In Population
- The carry capcacity of an ecosystem depends on numerous biotic and abiotic factors.
- These can be classified into two categories.
1. `Density dependent factors`
2. `Density independent factors`
## Density Independent Factors
- DIF’s can affect a population no matter what its density is. The effect of the factor (such as weather) on the size of the population **does not** depend on the **original size** of the population.
- Examples:
- unusual weather
- natural disasters
- seasonal cycles
- certain human activities—such as damming rivers and clear-cutting forests
## Density Dependent Factors
- DDF’s affect a population **ONLY** when it reaches a certain size. The effect of the factor (such as disease) on the size of the population depends on the **original size** of the population
- Examples:
- Competition
- Predation
- Parasitism
- Disease
## Relationships
1. **Symbiosis**
- Two different organisms associate with each other in a close way.
- Is the interaction between members of `two different species` that live together in a close association.
- Types
- **Mutualism (+/+)**
- Both species benefit from the relationship.
- (eg. human intestine and good bacteria, bees and flowers, clownfish and sea anemone, cattle egret and cow).
- **Commensalism (+/0)**
- one species benefits, the other is **unaffected**.
- (eg. beaver cutting down trees, whales and barancles).
- **Parasitism (-/+)**
- one species is harmed, the other **benefits**.
- (eg. lice and humans, mosquito and humans).
- **Competition (-/-)**
- neither species benefits. Can be harmed. (-/-).
- **Neutralism (0/0)**
- both species are unaffected (unlikely).
- True neutralism is extremely unlikely or even impossible to prove. One cannot assert positively that there is absolutely no competition between or benefit to either species.
- Example: fish and dandelion
| + | Parasitism and Predation | Commensalism | Mutalism |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Neutralism | Commensalism | |
| - | Competition | Parasitism and Predation | |
| - | 0 | + |
 ## Ecosystem Services
- **Cultural Services**
- Benefits relating to our enjoyment of the environment.
- Ex. Recreational, aesthetic and spiritual experiences when we interact with natural surroundings.
- Ecotourism: tourists engage in environmentally responsible travel to relatively undisturbed natural areas.
- Ex. Canada’s Wilderness.
- **Ecosystem Products**
- Humans use products produced by the ecosystem.
- Hunt animals and harvest plants, lakes/oceans supply us with seafood.
- **Terrestrial:** ecosystems: medicines, fibres, rubber and dyes.
- **Forestry**: largest industries and employers.
- Regulate and maintain important abiotic and biotic features of environment.
- Cycle water, oxygen, and nutrients.
- Help protect us from physical threats.
- Plant communities protect the soil from wind and water erosion.
- Ecosystems act as sponges.
- Absorb water and slowly release it into the groundwater and surface water (reduces erosion and protects against flooding, filters the water).
- Protect land from storms along coasts where wave damage erodes the shoreline.
- Mangroves
### Monetary Value of Ecosystem Services
- Very difficult to put a dollar value to it.
- Dollar value of cleaning the air/water, moderating climate and providing paper fibre, medicines and other products is HIGH.
- Ranges into the trillions of dollars/year (maybe 60 trillion?).
- Provides valuable services that are free and renewable.
## Successions
- Natural ecosystems are in a state of equilibrium (their biotic and abiotic features remain relatively constant over time).
- Equilibrium is established when abiotic conditions are stable.
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are balanced.
- Populations are healthy and stable.
- Small ecosystems are in a constant state of change.
- Forest fire or disease outbreak can cause short-term changes on a local level.
- Types
- #### Primary
- on newly epxposed ground, such asa following a volcanic eruption.
- #### Secondary
- in a partially distrubed ecosystem, such as following a forest fire.
- Human caused disturbances.
- Results in gradual changes as plants, animals, fungi and micro organisms become established in an area.
- In both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
### Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosystems maintain their long term sustainability.
- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused disturbances.
- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rico).
- Time needed is very long.
- Original cause of disturbance must be eliminated.
- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
- Disturbances can be repaired through human actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Species at Risk
- Do not have to be driven to extinction for there to be ecological consequences.
- Population falls below critical level = ecological niche can no longer be filled.
- Consequences for abiotic and biotic features.
- **Extirpated**: no longer exists in a specific area.
- **Endangered**: facing imminent extirpation or extinction.
- **Threatened**: likely to become endangered if factors reducing its survival are not changed.
- **Special Concern**: may become threatened or endangered because of a combination of factors.
## Ecosystem Services
- **Cultural Services**
- Benefits relating to our enjoyment of the environment.
- Ex. Recreational, aesthetic and spiritual experiences when we interact with natural surroundings.
- Ecotourism: tourists engage in environmentally responsible travel to relatively undisturbed natural areas.
- Ex. Canada’s Wilderness.
- **Ecosystem Products**
- Humans use products produced by the ecosystem.
- Hunt animals and harvest plants, lakes/oceans supply us with seafood.
- **Terrestrial:** ecosystems: medicines, fibres, rubber and dyes.
- **Forestry**: largest industries and employers.
- Regulate and maintain important abiotic and biotic features of environment.
- Cycle water, oxygen, and nutrients.
- Help protect us from physical threats.
- Plant communities protect the soil from wind and water erosion.
- Ecosystems act as sponges.
- Absorb water and slowly release it into the groundwater and surface water (reduces erosion and protects against flooding, filters the water).
- Protect land from storms along coasts where wave damage erodes the shoreline.
- Mangroves
### Monetary Value of Ecosystem Services
- Very difficult to put a dollar value to it.
- Dollar value of cleaning the air/water, moderating climate and providing paper fibre, medicines and other products is HIGH.
- Ranges into the trillions of dollars/year (maybe 60 trillion?).
- Provides valuable services that are free and renewable.
## Successions
- Natural ecosystems are in a state of equilibrium (their biotic and abiotic features remain relatively constant over time).
- Equilibrium is established when abiotic conditions are stable.
- Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are balanced.
- Populations are healthy and stable.
- Small ecosystems are in a constant state of change.
- Forest fire or disease outbreak can cause short-term changes on a local level.
- Types
- #### Primary
- on newly epxposed ground, such asa following a volcanic eruption.
- #### Secondary
- in a partially distrubed ecosystem, such as following a forest fire.
- Human caused disturbances.
- Results in gradual changes as plants, animals, fungi and micro organisms become established in an area.
- In both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
### Benefits of Succession
- Provides a mechanism by which ecosystems maintain their long term sustainability.
- Allows ecosystems to recover from natural or human caused disturbances.
- Offers hope (New Orleans, New Jersey, Florida, Puerto Rico).
- Time needed is very long.
- Original cause of disturbance must be eliminated.
- Not all disturbances can be repaired.
- Disturbances can be repaired through human actions that support the natural processes of succession.
## Species at Risk
- Do not have to be driven to extinction for there to be ecological consequences.
- Population falls below critical level = ecological niche can no longer be filled.
- Consequences for abiotic and biotic features.
- **Extirpated**: no longer exists in a specific area.
- **Endangered**: facing imminent extirpation or extinction.
- **Threatened**: likely to become endangered if factors reducing its survival are not changed.
- **Special Concern**: may become threatened or endangered because of a combination of factors.