9.4 KiB
Study Sheet
Unit 1: Functions
Words to know:
linear relationquadratic relationvertex of a parabolaline of best fitaxis of symmetry of a parabolainterceptsLinear Relation: A relation which a single straight line can be drawn through every data point and the first differences are constant
Non - Linear Relation: A single smooth curve can be drawn through every data point and the first differences are not constant
Relations
- A relation can be described using
- Table of Values (see below)
- Equations
- Graphs (Graphing the equation)
- Words
- Table of Values (see below)
- When digging into the earth, the temperature rises according to the
- following linear equation: . is the increase in temperature in
- degrees and is the depth in meters.
Definitions
Parallel: 2 lines with the same slope
Perpendicular: 2 lines with slopes that are the negative reciprocal to the other. They form a 90 degree angle where they meet.
Domain: The ordered set of all possible values of the independent variable .
Range: The ordered set of all possible values of the dependent variable .
Continous Data: A data set that can be broken into smaller parts. This is represented by aSolid line.
Discrete Data: A data set that cannot be broken into smaller parts. This is represented by aDashed line.
First Difference: the difference between 2 consecutive y values in a table of values which the difference between the x-values are constant.
Collinear Points: points that line on the same straight line
Variables
Independent Variable: A Variable in a relation which the values can be chosen or isn’t affected by anything.
Dependent Varaible: A Variable in a relation which is dependent on the independent variable.
Scatterplot and Line of Best Fit
- A scatterplot graph is there to show the relation between two
variables in a table of values.
- A line of best fit is a straight line that describes the relation
between two variables.
- If you are drawing a line of best fit, try to use as many data
points, have an equal amount of points onto and under the line of best
fit, and keep it as a straight line.

How To Determine the Equation Of a Line of Best Fit
- Find two points
ONtheline of best fit - Determine the
slopeusing the two points - Use
point-slope formto find the equation of theline of best fit
Table of values
To find first differences or any points on the line, you can use a
table of valuesIt shows the relationship between the x and y values.
Use
Finite differencesto figure out if its quadraic or linear:- If the
first differenceis constant, then its linear. (degree of 1) - If the
second differenceis constant, then its quadratic. (degree of 2)
- If the
This is a linear function
x y First difference -3 5 -2 7 5-7 = 2 -1 9 7-9 = 2 0 11 9-11 = 2 1 13 11-13 = 2 2 15 15-13 =2 - The difference between the first and second y values are the same as
the difference between the third and fourth. The
first differenceis constant.
- The difference between the first and second y values are the same as
the difference between the third and fourth. The
This is a quadractic function
x y First difference Second difference 5 9 7 4 9-4 = 5 9 1 4-1 = 3 5-3 = 2 11 0 1-0 = 1 3 - 1 = 2 13 1 0-1 = -1 1 -(-1) = 2 - The difference between the differences of the first and second y
values are the same as the difference of the difference between the
thrid and fourth. The
second differenceis constant.
- The difference between the differences of the first and second y
values are the same as the difference of the difference between the
thrid and fourth. The
Tips
- Label your graph correctly, the scales/scaling and always the
independent variableon thex-axisand thedependent variableony-axis
- Draw your
Line of Best Fitcorrectly
- Read the word problems carefully, and make sure you understand it
when graphing things
- Sometimes its better not to draw the shape, as it might cloud your
judgement (personal exprience)
- Label your lines
Number of Solutions
Discriminant
The discriminant determines the number of solutions (roots) there are in a quadratic equation. are the
coefficients and constant of a quadratic equation:

Tips
- Read the questions carefully and model the system of equations
correctly
- Be sure to name your equations
- Label your lines
Definitions
Function: a relation which there is only one value of the dependent variable for each value of the independent variable (i.e, for every x-value, there is only one y-value).Vertical-line test: a test to determine whether the graph of a relation is a function. The relation is not a function if at least one vertical line drawn through the graph of the relation passes through two or more points.Real numbers: the set of real numbers is the set of all decimals - positive, negative and 0, terminating and non-terminating. This statement is expressed mathematically with the set notationDegree: the degree of a polynomial with a single varible, say , is the value of the highest exponent of the variable. For example, for the polynomial , the highest power or exponent is 3; the degree of the polynomial is 3.Function notation: . is called function notation and represents the value of the dependent variable for a given value of the independent variable .Transformations: transformation are operations performed on functions to change the position or shape of the associated curves or lines.
Working with Function Notation
- Given an example of , to get , we substitute the 3 as into the function, so it now becomses .
- We can also represent new functions, the letter inside the brackets
is simply a variable, we can change it.
- Given the example , if we want , we simply do .
Vertex Form
Vertex from: .- is the coordinates of the vertex
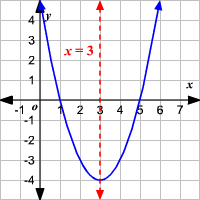
Axis of symmetry
- Example:
Direction of openning
- Given a quadratic in the from , if , the curve is a happy face, a smile. If , the curve is a sad face, a sad frown.
- Examples
- opens down, sad face.
- opens up, happy face.
Vertical Translations
Horizontal Translations
: absolute bracket.
- simplify and become positive
- (Multiply all the y-values from by a)
- (Not congruent to )
Example of stretching
- -Vertically stretch by a factor of 2
x y -3 9 (2)= 18-2 4 (2)= 8-1 1 (2)= 20 0 (2)= 01 1 (2)= 22 4 (2)= 83 9 (2)= 18- All y-values from are now multiplied by 2 to create
Example of compression
-
- Verticallyc ompressed by a factor of
x y -3 9 = 4.5 -2 4 = 2 -1 1 = 0 0 = 0 1 1 = 1 2 4= 3 9 = 4.5 - All y-values from are now multiplied by to create
-