46 KiB
Geography Study Sheet!!!!
Test Format
- Multiple choice
- True / False
- Matching
- Short Answer Questions
- Graphing & Analysis Questions
Bring to exam:
- course TEXTBOOK
- Pens, pencils
- Ruler
- Calaculator
BlueandRedpencil crayons- Eraser
Unit 1: Introduction to Cnanadian geography
(Chapter 1, pgs. 4- 16)
Terms
Absolute location: A location described in terms oflongtitudeandlatitude.
Relative location: A location described by in terms of its surronding features.
Geotechnologies
GPS: Global Positioning System- They tell us where we are
GIS: Geographic Information System- This technology is used to help geographers to anaylze an area of land
Telematics: The branch of information technology which deals with the long-distance transmission of computerized information.- This technology helps us to communicate between long distances
Remote Sensing: The scanning of the earth by satellite or high-flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it.- This technology helps us scan an area of land from a satellite
Geographic concepts:
Interrelationships: a relationship that exists betweeen different pattern and trends.- Example:
The mountain pine beetle is damaging the pine trees, we should are because our ecosystem and economics are also being damaged
- Example:
Spatial Significance: The importance of something’s location- Example:
Why are the pine beetles there? Due to climate change, they are surviving through the winter
- Example:
Patterns nad Trends: A recurring thing or change- Example:
Why things are there and why the matter
- Example:
Geographic Perspective: A geographic way of looking at the world- Example:
Geographers think about the ecosystem and the landscape while other people just regard them as mountains or rivers
- Example:
Unit 2: Interactions in the Physical Environment
(Chapters 1-4, pgs 18 - 100)Population Density:The number of people living in each unit of area (such as a square mile)CMA (Cemsus Metropolitan Areas): Area where alot of urban or people live (don’t know correct def)
Types of Populations
| Type of Population | Description |
|---|---|
| Dispersed | The population is very spread out acorss the land |
| Linear | The population is on some sort of striaght line, could be people all living across a river line |
| Concentrated | Alot of people in a small area, like
Toronto, very concentrated and has a very
high population density |
Theory of Continental Drift
- Plates move due to hot magma below it moving it
- It was theorized by German scientist
Alfred Wagner
Alfred Wegner’s Theory:
| Proof # | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. The Jigsaw Fit | He saw the jigsaw fit between South America and Africa, meaning they must have been together at some point |
| 2. Fossils | He found fossils of the same plants and animals on both continents, therefore it could’ve only happened if those continents were once part of the same land mass or joined together at some point |
| 3. The Mountains | The Mountains
(Appalachians, Caledonian and Scandinavia ) are similar in
age and structure on both side of the atlantic ocean, therefore the
mountains was made due to 2 of the continents when they collided |
| 4. Ice Sheets | Ice sheets were found in warm places, therefore the hypothesis is that these places were closer to the south pole at some point |
4 Geologic Eras
| Era | Dates |
|---|---|
Precambrian (Earliest Life) |
4600 to 570
million years ago |
Paleozoic (Ancient Life) |
570 to 245
million years ago |
Mesozoic (Middle Life) |
245 to 66
million years ago |
Cenozoic (Recent Life) |
66 to ? million
years ago |
Theory of Plate Tectonics
The cracked egg analogy- Basically the egg crackes are like the plates and the yolk is like
the hot magma moving the egg cracks
- Conventional Currents are the things that move the plates
Types of Plate Movements
| Type of Movement | Description |
|---|---|
| Divergent | When two plates move apart Most commonly happens around a mid ocean ridgeBoth plates get Larger when this happens |
| Convergent | Two plates move into each other 2 Types - Continental meets Oceanic: Oceanic slides
underneathContiental meets Continental: The bigger
slides underneath |
| Transform | When two plates move in a parallel
motion - it transforms their surrondings - Usually the main cause of Earthquakes |
Major Forces
| Type of Force | Description | Building up/Wearing down the land |
|---|---|---|
| Folding & Faulting | Folding rocks to produce mountains | Building up the land |
| Volcanism | Once magama settles, it dries and hardens to create new land masses or mountains | Building up the land |
| Erosion | Wearing away the Earth’s surface followed by the movement to other locations of materials that have worn away | Wearing down the land |
| Weathering | Breakdown of rock into small particles by rain, wind and ice | Wearing down the land |
| Glaciation | - When a large mass of ice moves across
the landscape if leaves a trail - It acts as a bulldozer, scraping the soil and rock, and picking up anything in its way - When the glacier stops, it leaves the pile of debris |
Wearing down the land |
More on Glaciation
Glacier: Great streams of ice that flows like water
Erosional Effects
1. Removal of Materials
- Soil and rocks
- Scrapes2.
Changes to Drainage Patters
- Completely changes patterns of ```rivers```, ```streams``` and ```lakes```Depositional Effects
1. By Ice
Type Description Till Plains Mixture of loose sediments and rocks of all sizes Moraines Tillsthat form at the edged nosed sides of a glacier
2. By Meltwater
Type Description Moving Water Moves glacial debris on a massive scale Still Water Meltwater formed into a lake
Silt and clay and other minerals are deposited
Types of Rocks
| Type of Rock | How They Form | Example(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Igneous | Formed when molten rock hardens | Granite |
| Sedimentary | Commonly contain fragements of other rocks compressed and cemented together | Limestone |
| Metamorphic | Formed when Igeneous or
Sedimentary rocks undergo heat and pressure to create a
different kind of rock |
Marble |
Rock Cycle
Landform Regions
| Region | Location in Canada | Prominent Features |
|---|---|---|
| Western Cordillera | - Yukon Territory - Northwest Territories - British Columbia |
- Formed when the
Pacific plate subducted under the
North American plate- It was formed during the cenozoic and mesozoic eras,
30 to 100 million years ago- Its very young- Highland |
| Interior Plains | - Northwest territories - Saskatchewan - Alberta - Manitoba - Nunavut |
Lowland |
| Innutian Mountains | - Nunavut | - Formed in mesozoic era - It was formed by the North American Plate- Its very young, hence higher- Lowland |
| Canadian Shield | - Northwest Territory - Nunavut - Saskatchewan - Manitoba - Ontario - Quebec - Labrador |
- Largest region |
| Hudson Bay - Arctic Lowlands | - Ontario - Quebec |
Lowland |
| Appalachins | - New Brunswick - Newfoundland - Nova Scotia - PEI |
Highland |
| Great Lakes - St.Lawerence Lowlands | - Ontario - Quebec |
Lowland |
| Region | Picture |
|---|---|
| Western Cordillera |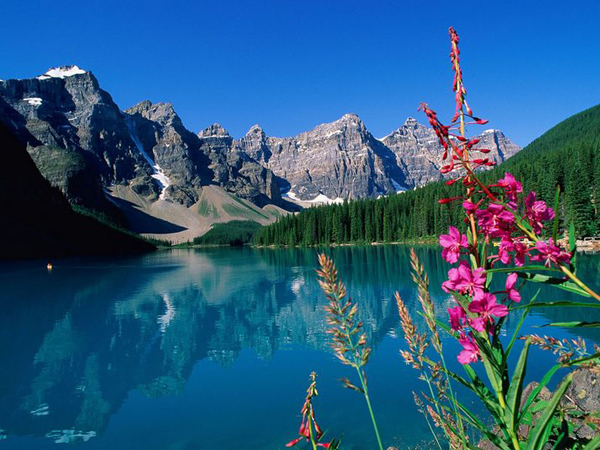  |
| Interior Plains |  |
| Canadian Shield |  |
| >> | Hudson Bay - Arctic Lowland |
| Appalachins |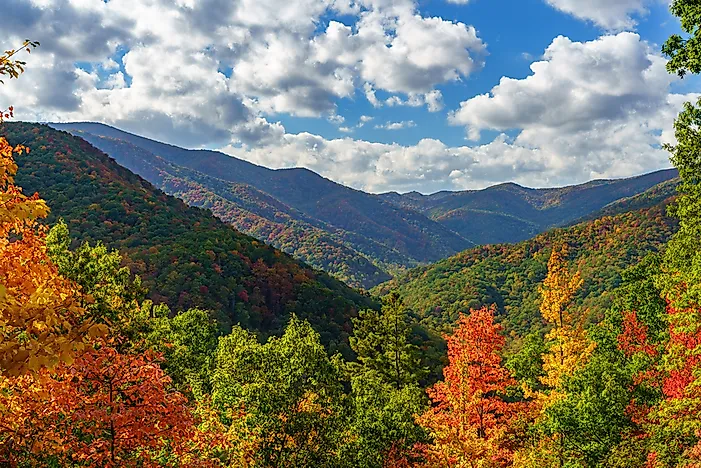  |
| Great Lakes - St.Laerence Lowlands |  |
Terms
Climate: The weather condition prevailing in an area in general or over a long period
Weather: The state of the atmosphere at a place and time as regardsheat, dryness, sunshine, wind, rain, etc
Prevailing Wind: Wind current that travels west to east
Climate graph
Percipitationon therightTemperatureon theleft- Use
blueforpercipitation - Use
redfortemperature - Label graph
- Month on bottom
- mm and degrees in their respective sides
- Title
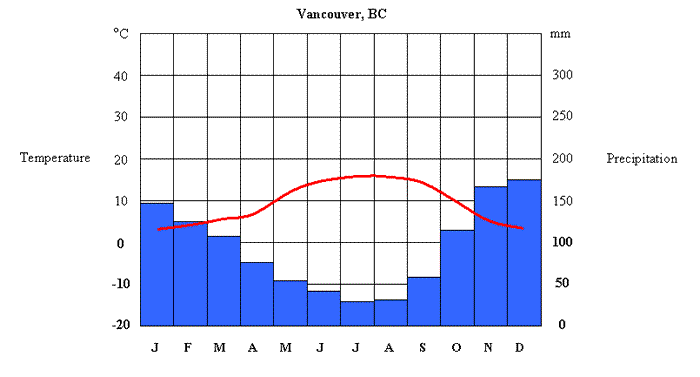
LOWERN
| Letter | Description |
|---|---|
| Latitude | - Where you are on a map - If you are farther away from the equator, the less direct sunlight you
receive, therefore it’s colder in that region |
| Ocean Currents | - Ocean currents moving away from the
equator is relatively warmer and currents moving towards
the equator is relatively cooler- Winds moving across the current are either cooled or warmed |
| Winds and Air Masses | - Air mass is a large volume
of air that takes on the climatic conditions of the area in
which it forms- They move depending on the weather patterns |
| Elevation | - It’s Colder the higher you
are |
| Relief | - Shape of the surface of the land - Affects precipitation- The side facing the wind gets more rain and snow- The opposite gets the rain shadow |
| Near Water | - Maritime climate- Winters are mild, summer never gets
too hot |
Continental v.s
Climate
| Type of Climate | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Maritime |
- Small annual temperature range (cool to
warm summers, cold to mildwinters) below 25C range- Annual percipitation is high - greater than
1000mm- Develops in coastal locations near major water bodies (i.e. Atlantic or Pacific Oceans) - Season of max precipitation is winter |
- Halifax - Nova Scotia - Vancouver - British Columbia |
Continental |
- Large annual temperature range (warm to
hot summers, cold winters) greater than 25C range- Annual percipitation is low - below
1000mm- Develops in area far from oceans and large lakes, in the interior of a continent/land mass - Season of max precipitation is summer |
- Regina - Saskatchewan - Winnipeg - Manitoba |
Climate Change
Causes
- Human activity
- Transportation
- Fossil Fuels
- Deforestation
- Appliances
- Garbage
Impacts / Effects
- Animals
- Fishes
- Sea Urchins
- Starfish
- Bear
- African Wildlife
- Polar Bears
- Feedback Loops
- Natural Diasters
- Temperature Rise
- Destroy Ecosystems
- Kills People
- Heat Strokes
- Natural Diasters
- Fires
- Deforestation
- The
Amazon Rainforestis becoming extinct
Solutions
| Solution # | Solution |
|---|---|
| 1. | Changing to LED lights |
| 2. | Solar Power |
| 3. | Turn theromo stats low |
| 4. | Turn off appliances |
| 5. | Drive less or get a fuel efficient car |
| 6. | Build Rigs to pump carbon
deep inside the Earth |
| 7. | Eat local food |
Local Level
- Carpool
- Public transportation(bus, subway)
- Eat locally produced food
- Conserve Energy (programmable, thermostat, unplug, appliances, LED, light bulbs)
- Electric car / Fuel efficient car
- Using cloth bags / reusable when going to the grocery store
- Compost
- Walk, bike to work / school
National Level
- Invest in green / renewable energies
(
wind, solar, geothermaletc) - Ban plastic bags
- Carbon tax
- Cap and trade programs (companies trade
GHGemissions credits) - Strict enviornmental laws regarding
GHGemissions by industry
Global Level
- Participate in
UN climate changeconferences - Countries promise to reduce
GHGemissions (ex.UN Paris Climate Change Agreement)
Greenhouse Gases
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect: Greenhouse gases created by human activity ### Main Greenhouse Gases- Methane
- Carbon dioxide
- Water Vapour
- Nitrous Oxide
Soil
Dry - climate(calcification)
Drysoil- Nutrients
rise upto the top layerTop soil is rich
Leeched
Wetsoil- Nutrients get
washeddown andawayPoor quaility soil
Vegetation In Canada
Region Description Tundra- Only a few very smalltrees grow here
- Small plants
-HarshconditionsBoreal and Taiga Forest- One of the largest forest regionin the world
Growing season gets longer fartherSouth
-LongandColdwinters
- Deciduous trees (White birch, Poplar)
-Poor quaility soilGrassland- Too dryfor tree growth
- Some trees
- Natural grasses grow taller in wetter areasMixed Forest- Mainly Deciduous
- A bit ofBorealin theNorthernarea
- Winters arecooland summers arewarm
- Soils are not as rich in theSouth, but morefertilethan theBoreal Forest
- Much of theSouth Mixed Foresthas been cleared foragricultureDeciduous Forest- Canada’s Tiny Deciduousforest region
-Hotsummers and relativelymildwinters
- Cleared for farming
- Soils arefertileWest Coast Forest- Large Coniferous species
- So muchPercipitationis called atemperate rainforest
Type of Tree Charateristics Examples Deciduous - The trees that drop their leavesduring the winter to survive
- Found intropicalclimates- Oak
- Maple
- Hickory treesConiferous - The trees that do not drop their leavesduring the winter
- Found in rathercoolerclimates- Cedar
- Douglas-fir
- Fir
Aboriginal People
Attawapiskat
- Main source of water for Attawapiskat First Nations is a murky lake full of
organic matter- Water
treatement plantsis not able to bring water to required standards for humans- Mainly rely on
bottled waterSewage systemdoes not work properly- Some families in
Attawapiskathave no access torunning waterat all
Unit 3: Managing Canada’s Resources and Industries
(Chapters 5-9, pgs. 101-201)
Resources
Type of Resource Definition Examples Renewable Resource that replaces itself unless badly mismanaged, are constantly being replenished by nature at a rate fast enough/faster than we are using.deplenishing them- Trees
- Fish
- SoilNon-Renewable Resource that can be used only once, they are created so slowly by nature that the stock today is all that there will always be- Oil
- Iron Ore
- Fossil FuelsFlow Are constantly being produced by nature. Their supply cannot be damaged by human activity- Sunlight
- Water
- Wind
The 3R’s
The R Description Recycle Recycling recyclableitemsReuse Reusing reusableitemsReduce Reducing the things that can be reduced
Farming
Problems
Loss of Farmland in Ontario
Description
- urban expanision is taking farmland away
Advantages/Attempts
- Greenbelt act and GTA growth plan will protect farmland in Southern Ontario
Disadvantages/Next Steps
- Protect forms or else Cnadaians will have a food crisis, where we run out of agricultural products
Solutions
- Create “smart” communities
- Densely packed fmarland, using up less space
Decline of the Family Farm and Growth of Agribusiness
Description
- Less family farms, more agribusiness (large companies)
- Better technology and smaller farms
Advantages/Attempts
- More food produced faster
- Less soil erosion
Disadvantages/Next Steps
- Pollution
- Broken realtionship between farmer and machine
- More GMOs
Solution
- Support more sustainable farmers
- Be aware
- Use corporate farms with family farm methods
Sustainable Agriculture
Description
- Unsustainable agriculutre damages environment too much
- manure leakage
- Chemicals
- Soil pollution
Advantages/Attempts
- Less damage to environment
- Less air, water, and soil production
- Fewer diseases and chemicals
Disadvantages/Next steps
- Chemical leakage in soil
- Contributes to global warming and GHGs
- Water, air and soil contamination
Solutions
- Have livestock facilities
- Nutrients management
- Be energy efficient
Organic Farming
Description
- Organic foods are being replaced by chemicals, fertilizers, antibiotics, animal cloning, and genetic modification
Advantages/Attempts
- Many people want to buy organic food productsfree of chemicals pesticides
- People like to try new products
- Some like to ensure products taste, concerns for the environment, and GMO prevention in foods
Disadvantage/Next Steps
- Expensive
- Labour-costly
- Skills are needed
- needs time to grow crops or livestoc naturally
Solutions
- Organic farming may increase in the future becuase people may see good in it
- May be just a trend
- May decrease due to the fact that it may be expensive and technology may be increasing
Mad Cow Disease (BSE)
Description
- Neurological disease
- Creates microscopic holes in the brain of affected cattle
- Gives brain spongy apperanace
- Spread by cattle feed from dead cows
Disadvantages
- Could heavily affect world trade due to infected meat
Solutions
- Canada accepts beeef from places that can consider and control BSE
- CFIA (Canadian Food Inspection Agency) banned the use of protein products from cattle, including brain, animal feed and fertilizers
GMOs (Genetically Modified Organisms)
Description
- Impacts the environment
- Sprayed with pesticides and end up in lakes or rivers
- Killing off bees and butterflies
Advantages/Attempts
- Insect resistance
- Drought tolerance
- Disease tolerance
- Reduced food waste
- Requires less labour
Disadvantages
- GMOs result in…..
- Tumors
- Damaged immune system
- Reproductive problems
- Allergies
Solutions
- GMO foods
- Organic
- Processed Foods
- Look for non-GMO project seals in grocery stores
Factory Farming
Description
- In the past, livestock was treated properly
- Now, they are being confined in small spaces where living conditions are terrible and diseases spread quickly
Advantages/Attepmts
- Farmers make profit
- Farmers can make more money
- More food being produced at a cheaper price
Disadvantages
- Animals are being treated poorly
- Animals kill each other
- Bad for environment
- Pollutes water system
Solutions
- Buy from fmaily farms
- Buy from industries that treat animals properly
- Raise awareness
Intensivev.sExtensive
Type Definition IntensizeLarge amountsoflabour, machinery and fertilizersused onsmallfarms.High yieldsper hectareExtensiveSmall amountsoflabour, machinery, and fertilizersused onlargefarms.Small yieldsper hectare
Forestry
Problems - Poor forestry practices - Soil Erosion
Type of Cutting Description Pros Cons Clear Cutting Clears an entire land of trees Very productive and efficient, Cheap Harms the environment too much Shelterwood Only cut down some species of trees Productive, less harm to the environment Costly Selective Cutting Only cut trees of the desired type, color quality etc Sustainable practice Not productive, Very costly
Clear-Cutting
- Use in most logging operations
Removeevery single tree, leaving barren landscape behind- Most trees are replanted in rows on columns so they can be later cut
uniformly and easily- If no replanting, less desirable species of trees may grow and soil erosion
Shelter wood
Clear cuttinggroups in a forest- Seed bearing ttrees are left standing so newer generations of trees can grow
- Seeds
regeneratelogged areas- Shelterwood is used in forests with trees around the
same age- Generations of
older and youngertrees is the result
Selective Cutting
Maturetrees are only cutDesired size, type of qualityis taken into accountLess disruptiveto the environment, butcostlyto find trees- Does not allow the replanting of a new
uniform forest
Fishing
East Coast Fisheries
Reasons why it collapsed
Uncontrolled Foreign FishingOverfishingImproved Fishing TechnologyDestructive Fishing PracticesChanges in Natrual Conditions
Offshorevs.InshoreFishing
Type of Fishing Description Pros Cons InshoreCommerical fishingcarried outclose to shoreinsmall, independently-ownedboats- Traditional
- LessDestructivethan offshore- Less Productivecompared to offshore
OffshoreCommercial fishingcarried outfar from shoreinlarger company-ownedboats- Very productive
-high profit
&ndsp;- Less Traditional
- MoreDestructivethan inshore
Water
Fresh Water:3%of the worlds water is freesh water
Water Issues
Uncleanandunsafewater
- We are
running outoffresh water, ordrinkablewater
Aboriginals and Water: Life on The Reserves
The abroginal people had to take water from nearby water sources
There wasn’t any waterTreatment plantsin their area Had tohunttheir own food most of the time (i.efish)
unsafeanduncleanwater
Grassy NarrowsandMercury Poisoning
Energy
Type Description Issues Fracking By pumping chemicals deep underground to generate fossil fuels It damages the environment and contaminates nearby water and land Fossil Fuel Non-renewable resources extracted deep underground Non-renewable resource
Conventionalv.sAlternativeSources > ## Conventional
Energy Source Description Advantages Disadvantages Coal Coal is formed from decayed plants and organic matter, which is then extracted
produces electricity using steam (thermoelectricity)
The steam is produced from burning the coal- Plants can be built near urban areas
- Keeps transportation costslow
-Low-cost plants
- Fossil fuels prices rise
-Non-renewable resource
- creates a lot ofair pollution
Oil & Gas It’s formed from decayed plants and organic matter, which is then extracted
produces electricity using steam (thermoelectricity)
The steam is made from the burning of oil & gas- Plants can be built near urban areas
- Plants can be built where fuel is rapidiyaccessible
- Cheap plants
- Fuel costs raise rapidly
- Uses annon-renewable resource
- Creates a lot ofair pollutionandacid percipitationFracking Creating natural gas by pumping chemicals deep underground
which is then extracted later and treated the same as fossil fuels and natural gases
- Dramaticallyreducing cost of naturallgas globally
-Reduces carbon emissions
- Contaminantes air and water
-Destructionof potiental farmlands
Nuclear It creates energy by spliting an atom, which gives off heat, which is then produced into steam to turn turbines to produce electricity
- Plants can be built easily where the energy is needed
- Operating costs arelow
- Abudant supply ofuranium
- Does not produceair or land pollution- Construction costs are very high
-Radioactivefuel is very hazardous tohuman-health
-Radioactivewaste have nowhere to go and aredangerous
- Reactors age and becomeunreliableHydroelectricity
Electricity is generated by the movement of water
This movement of water turns turbines which generates electricity
- Uses a flow resource
-Creates recreational activities
- Costly
-Flooding
-Dangerous chemicals
- May affect nearbyecosystems
Alternative
Enerdy Source Description Advantages Disadvantages Solar Uses the sunas a heat source to collect energy- Its is a reliable consitent supply
- Solar panels are becoming moreefficient
- It can be incorporated into the existingelectric grid
- It can be used on alocal scale- The sun does not shine all the time
- Solar energy is not uniformly delivered across Canada
- It’s adiffusesource that needsmany collectorsto generate enough power
Wind Uses the wind currentto turn turbines to generate energy- The costs of wind turbines are decreasing
- It can be incorpoarated into the existingelectric grid
- It can be used on alocal scale
- The wind does not blow all the time
- Wind is not uniformly delivered across Canada
- It’s adiffusesource that needsmany turbinesto generate enough powerTidal Uses The waves tidal forceto generate energy- It’s a reliable consitent supply
-Improved designsof generators are making more sites possible- There are few suitble sites
- Generating stations areexpensiveto build
- Building stations hasenvironmental impactsHydro See Conventional - Highly efficient
- It’s areliable, consistent supply
Building stations has environmental impacts
- Depends onextensize power grids
Minerals
Type Description Examples Metallic Minerals that when refined, gives us the metalgroupGold, Silver, PlatinumIndustrial (non-metallic) Minerals that are non metallic nor fossil fuel minerals Asbestos, Potash, DiamondFossil Fuels Minerals that release energy when burned Coal, Natural gas, Oil
Types of Mines
Type of Mining Description Strip Is used to mine coal, oil sands and other minerals that are located in horizontal layers near the the surfaceOpen-pit Is used to mine minerals that are found near the surface but may also extend deep into the groundUnderground Is used to extract minerals ores located deep underground
Types of Industries
Industry Definition Examples % of Workforce Primary Industries that take raw materials from the natural environment Agriculture, Mining, Forestry, Fishing etc4.1 Secondary Processing of primary industry products into finished goods Construction, manufacturing, making prodicts like pencils, skates, tables etc20.7 Tertiary Wide range of services that support primary & secondary industries and society in general Teachers, hair dressers, Programmer etc75.2
Terms
Free Trade: International trade without tarifs or other barries to trade
Tariff: A tax applied to imported goods that is designed to prouct domestic manufacturers by making foriegn goods more expensive
NAFTA: North American Free Trade Agreement
CETA: Canadian European Union Comprehensive economic Trade Agreement
Trade Surplus: The difference between theexportsandimportsif the exports exceed the imports
Trade Deficit: The difference between theexportsandimportsif the imports exceed the exports
Exports: Giving stuff away
Imports: Getting stuff in
Comparative Advantage: A situation in which a country is better off focusing its efforts in fields where itsmost competitive
Dutch Disease: A Situation in which th value of acountry's currencyis driven up by the growth ofexports of natrual resources, such asoil or mining
Multiplier Effect: The increase intotal wealth or incomethat occurs whennew moneyis injected into theeconomy
Unit 4: Changing Populations
(Chapters 10-11, pgs 212-254)
Terms
Birth Rate: Is the number ofbirthsper1000 people
Deat Rate: Is the number ofdeathsper1000 people
Doubling Time/Rule of 70: The amount of time it takes thepopulationtodouble
Immigration Rate: The number ofimmigratesper1000 people
Emmigration Rate: The number ofemmigratesper1000 people
Net Migration Rate: Theimmigration rateminus theemmigration rate
Population Growth Rate: Thenatural increaseplus thenet migration rate
Immigrant: People who moves to one country from another country
Emmigrant: People who leave one country to move to another country
Total Fertility Rate: Theaveragenumber of children born to awomanin alifetime
Natural Increase: The surplus / deficit ofbirths over deathsin a population in a giventime period
Dependency Load: The percentage of the population that isnon-working. It is conventionally defined as including peopleyounger than age 15 and older than age 65
Population Pyramids
Type Picture Expansive Stationary Constrictive
% of people is the
x-axiscolour your population bars with different colours for gender
Aging Population
Problem Description Healthcare - More hospitals/facilities need to be built
- More healthcare workers (nurse, doctors, technicians) will need to be hiredHousing - People may downsize their home (buy smaller houses)
-Bungalows and condosmay become more popular
- More seniors homes need to be built (nursing homes)People Available to Work
(The Workforce)- More people will be retiring
- Fewer Canadians paying taxesJob Opportunities for Younger Canadians - More jobs could open up as large numbers of seniors retire
- Jobs that focus on helping seniors like lawn services, senior travel agents andoptometristsSorts of Things Canadians Want to Buy - Clothing for mature tastes and sizes
- Health aids (hearing aids, eye-glasses, dentures etc)
- Styles of vehicles to suit older buyers
Double Line Graph
Chinas former One Child Policy
China only allowed
one childper family, this was used tocontrol the population
The result of this was way too manyboysas families wanted boys because they would stay with them and carry on their family name
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
- The development of agriculture
- The transition from rural to urban residence
- An increased awareness of disease prevention and cures
- Change in the societal role of females
- Changes in preferred family size
Stages
- Pre-Transition
- Both birth and death rates are
high
- Woman have
6 to 10children on average- Most children die before adulthood
- The population does not grow/grows
minimallyNo country is currently in this stage- Food is
huntedandgathered- Very
basic formsof agriculture- Life is
harsh and uncertainDiseases are very common and deadly- Most people die from
disease,poor nutrition, orcontaminated drinking water
- Early Transition
- Birth rates are
high, death rate dropsdramaticallyPopulation explosionVery few countriesare in this stage
- Examples:
Chad, NigerAgricultureis very common- Commercial food production
increasesLess diseasesdue to simple sanitation improvements- People begin
migratingtourbanareas- Large families persist, but less children die
- Late Transition
- Birth rate
drops quickly, death rate drops furtherSmall familiesare becoming the norm- The
natural increaserate (in population) drops- Most people live in
urbanareasMechanization, especially inagriculture
- Post Transition
- Birth rate and death rate
stabilizeto around the same level
- However the
replacement rate(number of births per woman that result in a stable population, is usually2:1) isdramtically declining- Alot of the population is
graying- More than
80%of the population is urban- Woman work
full-timejobs similarly to men
Push and Pull Factors
Push Factor: A reason that encourages people to move away from their current country - Examples:Undesired climate, threat of war, economic problems, poor environmental conditions
Pull Factor: A reason that makes particular country seem attractive to potential immigrants - Examples:Economic opportunities, political stability, freedom, residental friends and family
Type of Immigrants
Permanent
Type Description Skilled Worker Class - Judged using a point system. To be admitted into the country, they need a minimum number of points
- This point assessment is done for the family member with the highest point total
- If one person qualifies, whole family is let in
- Government has identified high-demand occupations like engineers, doctors, nurses etc.Skilled Trades Class - Attracts immigrants with specific trade skills that are in short supply in Canada (i.e. electricians, plumbers, machinists, mine workers)
- This is a “pass or fail” system rather than a point system
- Person must meet 4 requirements:
- Have a job offer in Canada
- Have strong enough language skills to do the job
- Have two or more years of experience in the trade
- Be qualified to do the job by Canadian standardsCanadian Exprience Class - Accepts immigrants who have legally worked in Canada under a temporary worker program for at least one year
- Pass or fail system, applicant does NOT require a job offer in CanadaStart-up Visa - To apply in this class, a person must want to start a business in Canada
- Applicants must meet 4 criteria to be accepted:
- Prove that approved Canadian investors will fund their business idea
- Be proficient in English or French
- Have at least 1 year post-secondary education (i.e. college, university)
- Have enough money of their own to support themselves until the business can support them
Temporary & Humanitarian
Type Description Temporary Foreign Worker Program - Fill Labour Shortages
- Extraordinary talents: enhance economy
- Some immigrate after the end of their contract as “Canadian Experience Class”
- Most return home after the end of their work VISA
- ControversialFamily Class - Allows families of Canadian citizens to reunite in Canada
- these immigrants must be sponsored by a family member living in Canada that is at least 18 years of age
- the sponsor must agree to provide housing and financial needs for the new immigrant for 3-10 years if they run into financial difficultyRefugees - A refugee is someone who fears persecution (or even death) in their home country
- this persecution must be for reasons of race, religion, nationality, or political opinion
- approximately 30 000 refugees are allowed into Canada every year
- a refugee would not be required to take the point system test
Rule: In canada,Economic immigrantsneed minimum 67 Points to be considered in Canada
Where are Immigrants coming from?
- Coming from: Mainly
China, Phillipines, and India (in order from most to least immigrants)- Settling in:
Ontario(28.5%),British Columbia(27.6),Alberta(18%),Quebec(12.6%),Manitoba & Saskatchewan(11.6%),Territories(6.9%),Atlantic Canada(4.1%)
- The most settled in cities:
Toronto, Vancouver, Calgary (in order from most to least immigrants)Distribution
- Economic Class:
62.7%- Family Class:
25.2%- Refugees:
9%- Other:
3.5%
Migration of FNMI
Aboriginals make up
4.3%of canadas population
Are not spread across the countryevenly```` - For example,16.2%of aboriginals reside inSaskatchewanandManitobacombined, while53.2%reside inthree territories```
Levels of Development
Developing
Lowest levelofeconomic and social development- Economy is largely dependent on
primary industries (farming, mining, fishing)- Manufacturing is becoming widespread
Tertiary and quaternaryindustries are scarce and underdeveloped- Citizens have a
low incomeand often do not pay taxes- Government has
minimal funding- Example Countries:
Mongolia, Ethiopia, Madagascar, Bangladesh, Kenya
Newly Industrializing
- In between developing and developed
- Secondary industries are becoming more common
(manufacturing, construction)Tertiary industriesare starting to appear- Often due to
social bias
- Examples:
Child labour, expensive healthcare- Example Countries:
India, China, Brazil, Mexico, Russia
Developed
Highest levelof economic development, social development, and standard of living- Economy is largely dependent on the
tertiary and quaternaryindustries- Manufacturing is less common but was widespread in the past
- Primary industries are the least prominent
- Example Countries:
Australia, Canada, United States, United Kingdom, Japan
Are increasingly moving to
urban areas- The land given through treaties and reserves is often ofpoor quality- Results in alack of jobs,overcrowded housing, andlack of resources- In Ontario,80%of FNMI liveoff-reserve
Scatter-graph
Graphing
- label x and y axis
- title
- appropriate scale
- plot points down
- line of best fit
Analysis
- Positive, Negative, No correlations
- Patterns and Trends
- Strong, weak line of best fit
Foriegn Aid
ODA
Official Development Assistance; the formal term for the aid provided by developed countries to poorer countries - Measured by comparing it to the size of a country’s economy -
Bilateral Aid: money from a country –> poorer countries -Mulilateral Aid:money from a country –> UN/NGO –> poorer countries
NGO
Non-Governmental Organization: A private, not-for-profit organization working to achieve particular social, environemental, or political goals Examples:Doctors without Borders,World Literacy Foundation,Red Cross
Unit 5: Liveable Communities
(Chapters 12-14, pgs.255-308)
Terms:
Liveability: All the characteristics of a community that contributes to the quality of life of the people who live there
Sustainability: Improving the quality of human life while living within the carrying capacity of supporting ecosystems
Carry Capacity: The ability of the environment to support a population without enviornmental damage
Urban Issues
Urban Sprawl: largely uncontrolled expanision of cities onto adjacent or rural lands
Urban Sprawl Impacts
- Traffic Congestion
- Over burderdend services
- Air Pollution
- Plannign for mass transit
- Managing wastes
- containing urban sprawl
Solutions
- HOV lanes: high occupancy vehicle lanes available to buses and passenger vehicles carry at least two people; designed to help move more people through congested areas
- Waste Management: extensive recyling and composting programs (ex. Ontario’s blue box)
- Smart Growth: A concept for urban exapansion that also preserves the natural environment
- Principles
- Develop in existing communities
- Make them compact instead of sprawling out
- Mix land uses
- Put homes stores, offices, and services in close proximity to reduce traffic, and increase walking / biking
- Create a range of housing opportunities
- Bring people of different ages, household types, incomes, ethnicities together
- Provide variety of transport choices
- Public transit
- Create places and routes for safe walking / biking
- Protect wildlife habitats
- natural corridors
New Urbanism: a movement to reform the design of physical communities - Ex. Vancouver
Sustainable Communities
Importance of Agriculture
- its important to protect farmland because farmland provides sustainable development.
- It helps ensure that we will have local sources of food in the future and not to rely as much on imported foods
Vertical Cities
- High rises and skyscrapers are being built in cities
- Advantages
- less land
- can be built higher
- accomadating alot of people
Eating Locally
Locavore: someone who eats locally grown foodAdvantages
Financialsupports for farmers- Better trust between
customerandsupplier- Healthier food,
less chemicals- Better Taste
- Lower price (bargaining)
- Less
environmentalload
Respsect for traditional lifestyle
Measuring Sustainability & liveability
Human Development Index: measure of the overall quality of life that combines measures of wealth, health and education (developed by the UN)
Gross National Happiness: measure of the happiness of a population
Gross Domestic Product Per Capita: gross national product per person; measure of the size of an economy in dollars divided by population
Ecological Footprint
Ecological Footprint: the amount of productive land needed to provide you with the goods you use and to absorb the waste you produce - How to Determine: - Transportation use - Water use - Space used for work/play - Money used - How far your food shipped - Amount of living space - Amount of garbage
Credits
Annika Yang (A.K.A
nii,Sith Lord)
Adeline Su
Magicalsoup (ME!!!)
Ms Lagis



